The 27th Conference of Parties will take place in Sharm el-Sheikh, an Egyptian coastal city, from November 6 to November 18, 2022. Over 190 nations will be represented at the conference, which will be presided over by Egypt’s minister of foreign affairs.

Conference of Parties?
The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) has produced the Conference of Parties . It is described as the apex body and highest deciding authority with relation to climate change in UNFCCC Article 7.2. At COP, there are representatives from every State that is a UNFCCC member. The Earth Summit or Rio Summit, also known as UNFCCC, was established in 1992 with the intention of stabilising GHG emissions. Annual meetings of COP take place. And the States have met annually since 1995 with the exception of 2020, which was moved to 2021 due to COVID-19. Berlin, Germany hosted the inaugural Conference of Parties in March 1995.
Some Of The Important Conferences of Parties Sessions?
- KYOTO PROTOCOL: COP-3
The Kyoto, Japan-based Conference took place in December 1997, and it went into effect in February 2005. It is an international treaty that expands on the goals of the UNFCCC, established in 1992, which is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Its comprehensive regulations, known as the “Marrakesh Accord,” were approved in Marrakesh, Morocco, in 2001.
The Kyoto Protocol intends to reduce developed country greenhouse gas emissions by 5% in 2012 compared to 1990 levels, which were eventually boosted to 18%. The common but differentiated responsibility principle serves as the cornerstone of this Protocol (different capabilities and so different responsibilities). The only pact with legally binding restrictions on GHG emissions is this one. It is targeting CO2, CH4, N2O, SF6, HCFs, and PFCs, as well as other gases. Additionally, nitrogen trifluoride was added to the list by the Doha Amendment to the Kyoto Protocol.
The Parties are classified as: Annex 1: Developed countries and Economies in Transition (EITs); Annex 2: Members of Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development; Annex B: Annex 1 parties having emissions targets for both the terms; Non-Annex 1: Primarily Low-Income Developing Countries; Least Developed Countries: Nations with few resources for climate change adaptation.
There are two commitment periods, from 2008 to 2012 and from 2013 to 2020. The first commitment period went smoothly, but the second one was a failure. To obligate Parties to pay for CO2 emissions beyond the end of the second term, the Lima Conference was held in 2014.
India rectified the Protocol in 2012 and as of now, 192 states are Parties to the Protocol. However, the US and Canada are not signatories to the Protocol. Additionally, if any post-Kyoto pact requires a reduction in CO2 emissions, China, India, and the US have indicated that they will not ratify it.
The terminologies which came with the Kyoto Protocol-
- Carbon Credits Trading- It refers to selling extra credits to other organisations. Carbon credits are authorizations for companies to emit GHG or CO2.
1 Credit is equivalent to 1 Ton of Carbon Dioxide Permit.
- Carbon Offset- Reducing GHG emissions to make up for emissions from other sources. It is quantified in tonnes of CO2.

- PARIS AGREEMENT: COP-21
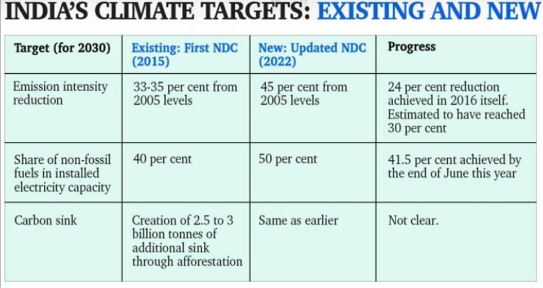
Occurred in December 2015 in Paris. The Kyoto Protocol will be replaced by the measures decided upon in this summit. It tries to unite all Parties under the UNFCCC for the same goal. It strives to maintain the temperature below 2 degrees and to limit it to 1.5 degrees above pre-industrial levels. to reduce emissions per unit of GDP by 33 to 35 percent from 2005 levels by 2030. Additionally, it made sure to produce 40% of the electricity from non-fossil fuels and use trees to sequester 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of carbon.
All of the Paris Agreement’s signatories, including India, will announce their action plans, or Nationally Determined Contributions. India joined as the 62nd country to ratify this Agreement in 2016.
- GLASGOW: COP-26
The Conference was originally slated to take place in Glasgow, Scotland in November 2020, however because of the COVID-19 epidemic, it was moved up to October 2021. By the middle of the century, it seeks to achieve net zero emissions while maintaining a 1.5% target. By 2020, it also hopes to mobilise around $100 billion in climate finance annually and safeguard and restore the ecosystem.
COP-27: SHARM EL-SHEIKH
occurrence in Egypt. It tries to carry out the decisions made at COP-26. And given that climate disasters are reaching historic proportions, this may be the ideal time to stop just talking and start doing. Additionally, now is the ideal time to concentrate on Non-Annex 1 nations and LDCs, where both adaptation and emission reduction are urgently needed. To direct climate funding, nations must speak with one voice to the international community.
Because carbon emissions are intimately correlated with everyone’s wellbeing, if the countries don’t take this issue seriously, it will harm all Parties concerned. And we don’t have to look very far to observe what happens to the world when nations fail to take the necessary actions at the appropriate moment, such as COVID-19.
read more : Glimpses of Indian Culture seen in World Dairy Conference represented in 50 countries













