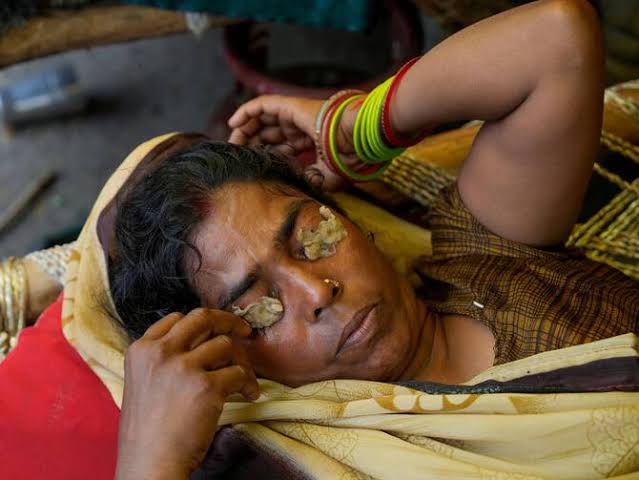
Delhi is witnessing a rise in cases of conjunctivitis, fungal infections, and vector-borne diseases, causing concern among health authorities. Health Minister Saurabh Bharadwaj has raised an alarm and alerted hospitals in the city about the rising number of cases. The spike in infections is being attributed to the prevailing high humidity levels. As a precautionary measure, the Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD) has issued guidelines to school teachers, urging them to be vigilant in recognizing conjunctivitis symptoms among students. Teachers have been advised to encourage good hygiene practices and discourage students from touching their eyes, face, or common surfaces with unwashed hands.
MCD’s Guidelines for School Teachers
In response to the growing incidence of conjunctivitis, the Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD) has taken proactive measures. The MCD recently issued guidelines to school teachers to help curb the spread of conjunctivitis among students. Recognizing that schools can be a breeding ground for infectious diseases, teachers have been advised to remain vigilant and promptly identify any student displaying symptoms of conjunctivitis. The common signs of conjunctivitis include redness in the eyes, excessive tearing, itchiness, and discomfort. By being alert to these symptoms, teachers can play a crucial role in preventing the spread of the infection among the student population.
Promoting Good Hygiene Habits
To further bolster efforts in controlling the outbreak, teachers are encouraged to educate students about the importance of practicing good hygiene habits. Proper handwashing is emphasized to reduce the risk of transmission through contaminated hands. Students are urged to refrain from touching their eyes, face, or any common surfaces with unwashed hands to prevent the spread of the infection. By promoting good hygiene practices, schools can create a healthier environment and minimize the chances of infectious diseases spreading.
Vector-Borne Diseases Surge
In addition to conjunctivitis and fungal infections, Delhi is also grappling with a surge in vector-borne diseases. Health authorities are reporting over 180 cases of dengue, surpassing the highest number of cases recorded in the past five years for the period from January 1 to July 22. Dengue is transmitted through the bites of infected mosquitoes, and its prevalence has been linked to the prevailing high humidity levels in the city. Apart from dengue, the city has recorded 61 cases of malaria and 14 cases of chikungunya, both of which are also vector-borne diseases transmitted through mosquito bites.
The Impact of High Humidity
The increase in humidity levels in Delhi has created favorable conditions for the proliferation of disease-carrying mosquitoes and fungi, contributing to the current outbreak. High humidity provides an ideal breeding ground for mosquitoes, allowing them to multiply rapidly and spread infections such as dengue and malaria. Furthermore, fungi thrive in humid environments, leading to an uptick in fungal infections. The Health Minister, Saurabh Bharadwaj, has highlighted the connection between high humidity and the rise in infectious diseases, urging citizens to take necessary precautions to protect themselves from these health hazards.
Health Authorities’ Vigilance
Given the severity of the situation, Delhi’s health authorities are closely monitoring the situation and implementing measures to combat the outbreak. Hospitals have been put on high alert to handle the increasing number of cases and provide necessary medical care. Health workers are conducting awareness campaigns to educate the public about the symptoms and preventive measures for various infections. The government is also focusing on mosquito control programs to reduce the mosquito population and minimize the transmission of vector-borne diseases.
In conclusion, Delhi is facing a critical health challenge with the surge in cases of conjunctivitis, fungal infections, and vector-borne diseases. High humidity levels have played a significant role in creating a conducive environment for the spread of these infections. By raising awareness and implementing preventive measures, the city’s health authorities aim to curb the outbreak and protect the well-being of the residents. However, individual responsibility is equally vital in maintaining good hygiene practices and taking necessary precautions to safeguard against these infectious diseases. As the situation continues to evolve, the collective efforts of the government, schools, and citizens are crucial in effectively managing and mitigating the impact of the ongoing health crisis.