According to the new RBI regulation for the protection of credit and debit card data, the real card details are swapped out for an alternative code called a token.

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is prepared to implement its card-on-file tokenization regulations as of October 1, after receiving several complaints about the abuse of debit or credit cards. According to a report by the news agency PTI, adding this layer of protection through tokenization is likely to improve consumers’ experiences with digital payments.
Because they had saved their card information on the merchant’s websites for future purchases, a number of customers have been taken advantage of by cybercriminals in recent years.
The deadline was extended in July by three months so that the industry could use the extra time to help all stakeholders get ready to handle tokenized transactions. Additionally, the extension was granted in order to raise public understanding of how tokens are created and how to use them in transactions.
What is the Tokenisation of Card Transaction?
Tokenisation is the process of replacing a card’s 16-digit number on the plastic card with a unique alternative card number, or ‘Token’ which shall be unique for a combination of card, token requestor and device. Tokens can be used for in-app purchases, web purchases, and mobile point-of-sale purchases. The most secure way to make payments is with this token since it never includes personal information that can be obtained directly and is constantly changing.
Benefits Of Tokenisation of Card Transactions:
- Tokenization aids in the security of data when it is in transit, at rest, and being processed for merchants and banks. To prevent security breaches, merchants keep tokens rather than credit card details in their POS systems, mobile wallets, and eCommerce platforms.
- It is inexpensive to comply with regulatory requirements using tokenization. By removing four PCI compliance requirements for retailers using tokenization, their operating costs are decreased.
- Customers simply need to enter their information once on an online platform. Furthermore, a dynamic token ID created at random and provided by the customer’s bank will be used in place of the real card number. This token ID is very hard to compromise or reverse-engineer.
- The costly procedures of notice, loss reimbursement, and legal action as a result of chargebacks are reduced with the use of tokenization.
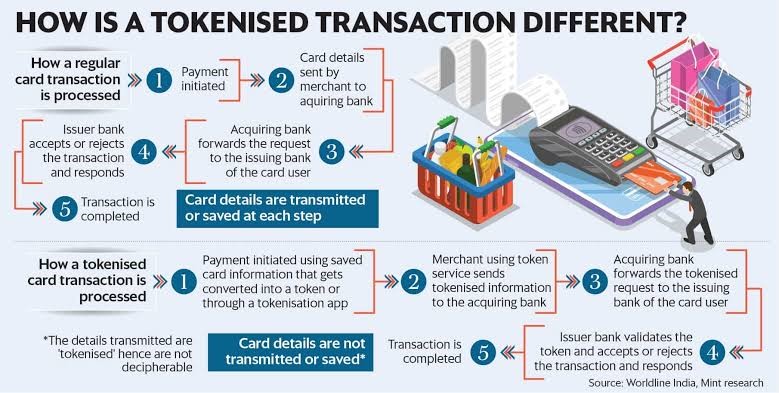
How tokenisation will work?
Previously, online platforms and shopping apps were able to store the card credentials of a customer.
Customers are prompted to enter their 16-digit debit card number followed by the CVV code when they make their first purchase on an e-commerce website. The 16-digit card number, however, is already kept on the website when customers purchase another item from the same platform, so consumers only need to enter the CVV; the bank will then produce the OTP.
With his new RBI order, a customer would be required to enter their entire card details while shopping. The merchant will start tokenization once consumers begin making purchases and will request permission before tokenizing a card. The merchant will submit the request to the card network after receiving approval.
The 16-digit card number will be replaced with a token that is created by the card network and sent back to the retailer. This token will be kept on file by the retailer for future transactions. They will now have to input their CVV and OTP, same as previously, in order to approve.
Since the campaign’s launch in December 2021, the Walmart-backed business claimed to have identified more than 80% of active user cards. Tokenisation substitutes a different code known as a “token” for the card number. Because the merchant is not given access to the real card details during the transaction, there is less potential for information leakage, making tokenized transactions more secure.
PhonePe had also said that the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) information security regulations had alerted it to 14 million credit and debit cards on its network.
Read more: Adani Enters the 4 Trillion Market Cap













