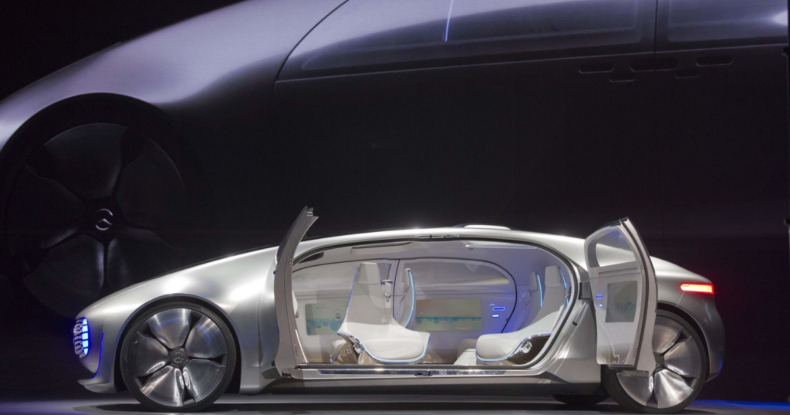
Cars are capable of sensing their environment and navigating without human intervention. It is estimated that by 2030, self-driving, or autonomous vehicles will constitute 25%. Companies like Google, Tesla, Mercedes, Ford, Nissan, Volkswagen, Hyundai, and others are leading the efforts by leveraging the latest technologies.
Experiments are going on autonomous cars, also called self-driving or driverless cars, globally. These cars can understand their environment and navigate accordingly.
India is far away from the long road while the world is about to commercialize self-driving cars. Autonomous cars must clear the policy decision, which is one of these cars’ hurdles before getting into the Indian market.
It is said that by 2030, self-driving cars will account for upto 25% of all the vehicles on the global road.
Self-driving cars use sensors and advanced technology to direct for a safe ride. In addition to reading road signs, they can detect the edges of the streets, traffic signals, and other vehicles using multiple video cameras and sensors in these cars.
These data are processed in a central control system which later controls the steering and the movement of the car at a safer distance from other vehicles.
The latest technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning and robotics engineering are leveraged by companies such as Google, Tesla, Mercedes, Ford, Nissan, Volkswagen, Hyundai, and others. Many startups in India are also experimenting with self-driving technology.
IN FAVOUR
Human error is estimated to cause nearly 80% of car crashes. Human error can be eliminated by self-driving cars, thereby reducing the number of accidents.
Autonomous cars can help people with special needs drive safely on the road. With them, they do not need assistance. There will be a high number of driverless electric vehicles (EVs) in the country, which will reduce pollution levels, which are also one of the significant issues the country faces.
The vast majority of Indians drive a long distance to work, often navigating heavy traffic along the way. During this time, they will be able to work on driverless cars.
In self-driving cars, the ability to communicate between them is an advantage. With real-time communication, cars could travel at optimal distances.
AGAINST
There are many types of vehicles on Indian roads, such as auto-rickshaws, rickshaws, handcarts, trucks and cycles, and animals like cows, camels and elephants. In this environment, technology cannot work smoothly.
New service stations need to be set up to maintain these cars, which would be costly, given the current state of the economy.
A traffic police officer directs traffic in traffic jams or traffic light failures. However, the problem remains that these cars cannot comprehend human signals, posing a problem when driving alongside conventional vehicles.
Further, autonomous vehicle technology can negatively affect the country’s unemployment problem. Self-driving cars may be susceptible to hacking. All automated vehicles must use the same networking protocol to communicate and coordinate.
GPS will not be followed by driverless cars. There are no potholes, recent changes, new signs, etc., taken into account by GPS tracking. An autonomous vehicle would not perform this function without human intervention.
CONCLUSION
In addition to reducing accidents, self-driving cars simplify driving. However, they can also be hacked. However, technology can overcome other shortcomings.
In an economy with a significant rate of unskilled labor, such as India, where the working population is high, introducing driverless cars may be risky.
The technology industry is a growing area that produces jobs in one sector and creates unemployment in another. There will be opportunities for other individuals involved in producing autonomous cars if it impacts drivers or public transportation.