There is mounting evidence linking sugar consumption and psychological distress.Sugar is addicting, alters the gut flora in undesirable ways, and may have deleterious effects on brain functionality.
- Functioning of brain via chemicals
- When it comes to the brain, sugar may have both positive and harmful effects.
- How sugar consumption affects our Hormones
When we gain new knowledge or have a good emotional response, the brain’s reward system is activated. Several areas of the brain communicate with one another and use chemical messengers to assist us in learning and practising tactics that improve our intelligence and well-being.
The reward system, which is primarily reliant on the neurotransmitter dopamine, explains a variety of commonly recognised human actions like as falling in love, enjoying sexual pleasure, and having fun with friends.
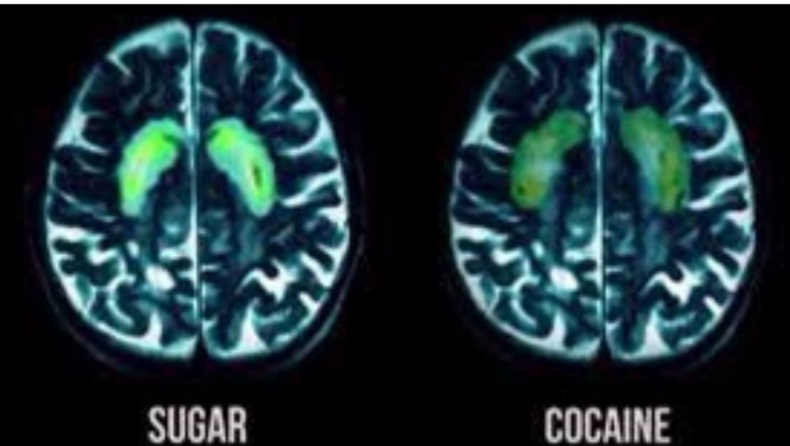
Cocaine, on the other hand, can “artificially” stimulate the brain’s reward system by “hijacking” it. Addiction develops when the brain gets impulses to engage in behaviours that produce a pleasure experience on a regular basis.
In a similar vein, sugar addiction develops.
Chemistry of sugar
Sugar’s propensity to both make us happy and sad can be explained by how the brain processes the sweetener. Sugar enhances the action of a critical neurotransmitter known as dopamine, resulting in transient emotions of reward and desire.
The brief rise of feel-good molecules like as endorphins and endocannabinoids is one of dopamine’s many impacts. This indicates that the favourable feelings of exhilaration and stress alleviation associated with consuming sugary foods are real, but transient.

Also, when the occasional treat grows into a regular diet of added sugars (more than 75% of foods in a normal grocery store today include added sugars), two molecular repercussions occur that diminish happiness:
The more we rely on dopamine to feel good and avoid feeling terrible, the less we are able to make serotonin.furthermore, if we rely on hormone reactions that prolong cravings and negative emotions over time, the more we rely on dopamine.
Serotonin is the neurotransmitter responsible for feelings of happiness, self-confidence, and overall fulfilment and antidepressants and psychedelics both increase serotonin activity in the brain. Similarly the sugar acts with dopamine.
Explaining leptin and its effects on the human body
Hormonal oscillations are a key but seldom discussed process through which a high-sugar diet causes negative sensations.
The majority of people are aware that sugar increases insulin levels. Insulin is a powerful anabolic (muscle-building) hormone that controls appetite and body fat.
Insulin and the hunger hormone leptin work in tandem.
Leptin is a hormone secreted by fat cells that alerts the brain that food is abundant.
The brain of a person who is underweight is more sensitive to the hormone leptin.
When leptin levels rise, the brain receives the information that it is full and thus burns more calories. However, increased insulin, which is observed in individuals with metabolic problems or who ingest an excessive quantity of sugar, decreases the brain’s sensitivity to leptin.
This condition is defined by leptin resistance. This suggests that even when leptin levels are high, the brain interprets them as low. When our leptin levels are low (as they would be on a crash diet) or when we acquire leptin resistance, negative emotions are a common symptom.
Real-time monitoring of leptin levels and emotions, for instance, reveals correlations as high as 0.70 between low leptin/leptin resistance and negative emotions such as anxiety and depression. In statistical parlance, a correlation of 0.70 represents an incredibly large effect size.
Functional connectivity in the brain, which links brain regions that share functional properties, and brain matter can be disrupted by high blood glucose levels.
In severe cases, it can lead to a loss of brain tissue and function. It can also cause small-vessel disease, which limits blood supply to the brain, leading to memory loss and, in extreme cases, vascular dementia.
In order to feel and perform at our best, consuming less sugar is essential.
Read more: https://tdznkwjt9mxt6p1p8657.cleaver.live/diabetes-a-rising-menace-in-india-2021/