“Nanobot” short for Nano Robotics is an emerging Nanotechnology field creating machines or robots.
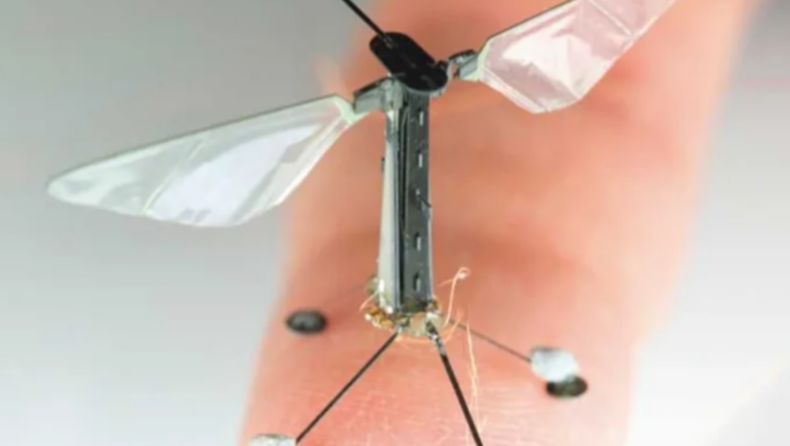
The world’s most miniature flying robot is the ‘RoboBee’ developed at the Wyss Institute, Harvard. It’s the size of your fingernail but needs to be tethered to a cable to power its wings. The smallest crawling, untethered micro-robot is only 0.2mm long.
Scientists in Germany took a step forward working on “nanobots” when they created a heat-powered motor using a single vibrating atom trapped in a nano-sized cone of electromagnetic radiation. Amazingly, it has the same working principles as a car engine: expanding, cooling, contracting, then heating.
Nanorobotics theory:
Manufacturing nanotechnology and nanomachines assembled from molecular components is a very challenging task.
- Biochips: The joint use of nanotechnology, nanoelectronics, photolithography, and new biomaterials provides a possible approach to manufacturing nanotechnology, nanorobots for common medical services, such as surgical instrumentation, diagnosis, and drug delivery
- Nubots: A nucleic acid robot (nubot) is an organic molecular machine at the nanoscale.[43] DNA structure can provide means to assemble 2D and 3D nanomechanical devices. DNA-based machines can be activated using small molecules, proteins, and other molecules of DNA.
- Retroviruses: They can be retrained to attach to cells and replace DNA. They go through a process called reverse transcription to deliver genetic packaging in a vector.[59] Usually, these devices are Pol–Gag genes of the virus for the Capsid and Delivery system
Designing of Nanobots “Nano Robotics”:
The robot allows precise interactions with nanoscale objects or can manipulate with nanoscale resolution.

Such devices are more related to microscopy or scanning probe microscopy, instead of the description of nanorobots as molecular machines, macroscale robots or microrobots that can move with nanotechnology precision can also be considered nanorobots.
Such an approach will not work due to the high surface energy of nanostructures, which means that all contacting parts will stick together following the energy minimization principle.
The adhesion and static friction between parts can easily exceed the strength of materials, so the parts will break before they move relative to each other.
This leads to the need to design movable structures with minimal contact area. In spite of the fast development of nanorobots, most of the nanorobots are designed for drug delivery purposes, and there is “still a long way to go before their commercialization and clinical applications can be achieved.
Read Also: Technology – effective and efficient way to communicate













