Sumerian and Harappan civilization is the world’s earliest civilization, which is known as Mesopotamian Civilization. City life began in Mesopotamia. The land between the river Euphrates and river Tigris is ancient Mesopotamia, now part of Iraq.
Introduction:
Studies of hundreds of Mesopotamian statues, ornaments, buildings, graves, tools & seals, and thousands of written documents took place. Mesopotamian civilization is mainly known for its writing system and its prosperity, city life, rich literature, and achievements in the field of astronomy and mathematics.
The Indus River Valley Civilization, 3300-1300 BCE, otherwise called the Harappan Civilization, stretched out from cutting-edge upper east Afghanistan to Pakistan and northwest India. Significant developments of this human progress incorporate normalized loads and measures, seal cutting, and metallurgy with copper, bronze, lead, and tin. Little is perceived about the Indus content, and therefore, little is thought about the Indus River Valley Civilization’s foundations and frameworks of administration. Human progress is probably finished because of environmental change and migration.

INSIGHT OF SUMERIAN CIVILIZATION:
In the North, there is Steppe, where herding provides people with a good livelihood rather than agriculture. In the east, the Tributaries of the river Tigris offer the route for the flow of Trade and Communication to Iran.
In the south there is a desert, this was the place where the first cities and writing emerged. This region supports life in the cities because of the deposition of lots of slits by river Tigris and Euphrates rising in the Northern Mountains that led to the fertility of the soil. When the Euphrates enters the desert it gets separated into small channels which act as irrigation canals for wheat, barley, peas, or lentils when required.
The agriculture of southern Mesopotamia was the most productive, of all ancient systems, even though it didn’t have sufficient rainfall for the production of crops, (including the ancient Roman Empire).
Not only in agriculture, Mesopotamian people were also engaged in non-agricultural activities in the North people were engaged in herding because of the presence of plains in the North and North-Eastern mountain slopes, production of wool, but meat and milk also took place. Rich production of agriculture and availability of resources also led to trade and communication with neighboring cities and places.
Both the Tigris and Euphrates paved the way for trade and communication. Thus, the climate and geographical proximity of the Mesopotamian region were highly productive and supported the settlement of cities.
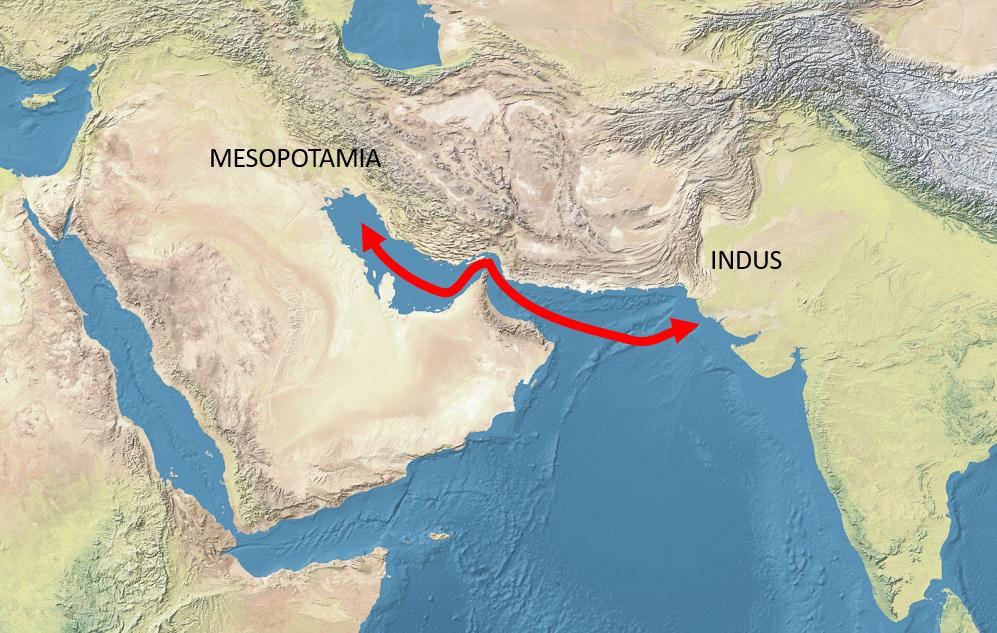
CONTRAST BETWEEN SUMERIAN AND HARAPPAN CIVILIZATIONS
The Indus Valley human progress thrived somewhere in the range of 2600 and 1900 BCE, around a similar time as civic establishments in Egypt, China, and Mesopotamia. The presence of huge streams like the Indus, Nile, Huang He, Yangtze, Tigris, and Euphrates made inactive conditions for endurance, agribusiness, and taming. These human advancements exchanged with one another and had social trades. Despite the fact that there are various likenesses, yet Indus Valley Civilisation was particular from different human advancements in the accompanying manners:
Geological Extent
The Harappa human advancement was multiple times more noteworthy than Egypt and multiple times bigger than the consolidating zone of Egypt and Mesopotamia.
Consumed blocks utilization
Burnt blocks were utilized astoundingly in development of structures in Harappa, while Egypt utilized dried blocks for a similar reason. Consumed blocks were additionally utilized by Mesopotamia yet Harappan urban areas utilized them to a great extent.
POLITICAL ASSOCIATION
There is no away from the political association of the Indus Valley individuals. In contrast to the Mesopotamians and the Egyptians, there is no proof of any engraving portraying their arrangement of organization. The steatite sculpture of the minister ruler demonstrates that the Indus valley individuals were more worried about business and they were administered by a class of traders.
TEMPLES
Rather than Egyptian and Mesopotamian human advancements, the Indus Valley Civilization appears to have come up short on any sanctuaries or huge royal residences that would give away from strict rituals or explicit divinities. In Egypt, a girl acquires the seat or property yet there is no proof that recommends that Harappa resembles Egyptians were matriarchal or not.
SOCIETAL NORMS
Training of creatures: Harappans in Gujarat tamed elephants which weren’t in Mesopotamian urban communities. Because of particular topographies and restricted interconnectedness, these civic establishments contrast in socio-social practices and even the degree of progression too.
SOURCE: ASIAVILLE
REFERENCE:












