Corbevax is now approved as a booster dose for adults with other COVID-19 vaccinations
A significant move by the Center is the first time in the country that a booster dose is different from the one that is used for primary vaccination against Covid-19.
According to Union Health Secretary Rajesh Bhushan, the Centre has approved Biological E’s Corbevax as a precautionary dose after six months from the date of administration of the second dose of either Covaxin or Covishield vaccines for the population over the age of 18.
The latest move by the Center, which comes amid an increase in Covid-19 cases in many states, is significant because it is the first time in the country that a booster dose is different from the one used for primary vaccination against Covid-19 has been permitted.
The union health ministry announced on Wednesday that Biological E’s covid-19 vaccine—Corbevax—will now be available as a precaution/booster dose for all adult individuals who have been fully vaccinated with Covishield or Covaxin. For a booster dose, Corbevax offers a heterologous covid-19 vaccine.
The Center also stated that all necessary changes have been made on the Cowin portal for the administration of heterologous precaution doses using Corbevax to those who are eligible and due for precaution dose. This option will be available from Friday, August 12th.
We have decided to further redefine precaution dose administration under the Covid-19 vaccination programme in light of scientific evidence, global practises, and domain knowledge experts’ recommendations. It is to inform the public that for those over the age of 18, Corbevax will be available as a precautionary dose 6 months or 26 weeks after the second dose of either Covaxin or Covishield vaccine. This allows Corbevax heterologous covid-19 vaccines to be used for precautionary dose administration in this age group,” Rajesh Bhushan, Union Health Secretary, said.
On June 4, the Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) approved Corbevax as a precautionary dose for people aged 18 and up. Bhushan also stated that the existing guidelines for homologous precaution dose administration of the Covaxin and Covishield vaccines will not be changed. “In addition to the existing homologous precaution dose, all persons over the age of 18 would have the option of a heterologous precaution dose with Corbevax,” he explained.
So far, more than 207.03 crore vaccine doses have been administered in India as part of the nationwide covid-19 vaccination drive. According to data released by the health ministry, approximately 97% of the population over the age of 12 have received at least the first dose. Furthermore, 89% of the intended population received both doses.
News agency PTI earlier reported that the Union health ministry had taken action after the recommendations made recently by the COVID-19 Working Group of the National Technical Advisory Group on Immunization (NTAGI).
Corbevax, India’s first indigenously developed RBD protein subunit vaccine, is currently being used to inoculate children in the age group of 12 to 14 years under the immunization program.
The COVID-19 Working Group (CWG), in its July 20 meeting, reviewed data from the double-blind randomized phase-3 clinical study which evaluated the immunogenicity and safety of a booster dose of Corbevax vaccine when administered to COVID-19-negative adult volunteers aged 18-80 years previously vaccinated with two doses of either Covishield or Covaxin.
India began administering precautionary doses of vaccines to healthcare and frontline workers and those aged 60 and above with comorbidities from January 10.
The country began inoculating children aged 12-14 from March 16 and also removed the comorbidity clause making all people aged above 60 eligible for the precautionary dose of the Covid vaccine.
India on April 10 began administering precautionary doses of vaccines to all aged above 18 years.
(With inputs from PTI)
COVID VACCINES IN INDIA
There are 11 Vaccines Approved for Use and 16 Vaccines in Clinical Trials in India.
How Vaccines Work
SARS-CoV-2 is the virus that causes COVID-19. The spike protein on the surface of SARS-CoV-2 is an example of an antigen.
Vaccines are the best way to train our immune system to recognize viruses, or pieces of viruses, called antigens. Our immune system creates antibodies and other defenses to protect us.
When a vaccinated person is exposed to SARS-CoV-2, their immune system will recognize the viral antigens and spring into action to keep them healthy. There are many different types of vaccines, as seen in the diagram below.
Types of Vaccine Platforms
All vaccine platforms are designed to train our immune system. There are two categories of COVID-19 Vaccines: Component Viral Vaccines and Whole Virus Vaccines.
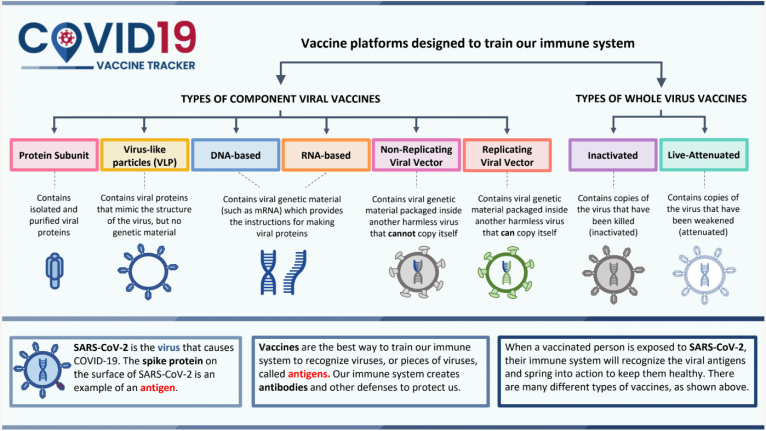
Component Viral Vaccines
- Protein Subunit: Contains isolated and purified viral proteins
- Virus-like Particles (VLP): Contains viral proteins that mimic the structure of the virus, but no genetic material
- DNA-based and RNA-based: Contains viral genetic material (such as mRNA) which provides the instructions for making viral proteins
- Non-Replicated Viral Vector: Contains viral genetic material packaged inside another harmless virus that cannot copy itself
- Replicating Viral Vector: Contains viral genetic material packaged inside another harmless virus that can copy itself
Whole Virus Vaccines
- Inactivated: Contains copies of the virus that have been killed (inactivated)
- Live-Attenuated: Contains copies of the virus that have been weakened (attenuated)
Source: COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker