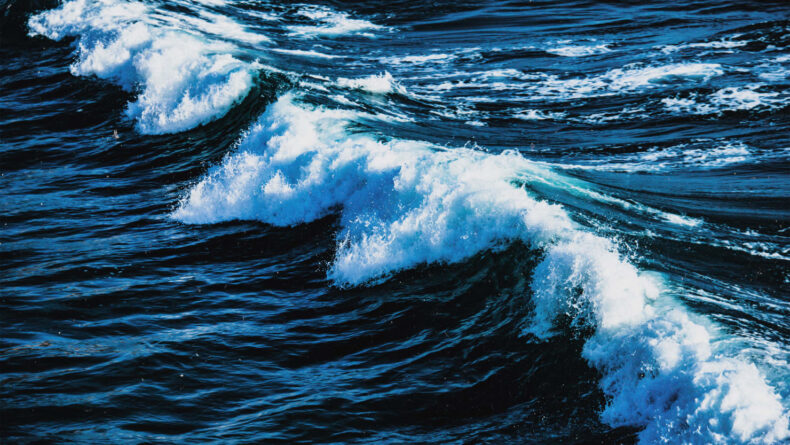
The findings of a recent study, published on Tuesday, have raised significant concerns about the stability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC). This immense system of ocean currents plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate by transporting warm water from tropical regions into the North Atlantic. However, the study warns that human-caused climate change poses a severe threat to its integrity.
Source: Science News
As a result of human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, the planet has been experiencing an increase in greenhouse gas emissions, leading to global warming. This, in turn, has far-reaching effects on various natural systems, including ocean currents like the AMOC. The excess heat trapped in the atmosphere is being absorbed by the oceans, causing the water in the North Atlantic to become warmer.
The study indicates that if current trends continue, the AMOC could reach a tipping point as early as 2025. At this critical juncture, the circulation pattern could weaken significantly or even collapse entirely, disrupting the delicate balance of the Earth’s climate system. The consequences of such a collapse would be far-reaching and impactful on a global scale.
One of the primary concerns is the potential alteration of weather patterns. The AMOC plays a key role in distributing heat around the planet, influencing weather conditions in various regions. Its failure could lead to disruptions in weather patterns, possibly causing more frequent and intense storms, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme temperature fluctuations in affected areas.
Moreover, the AMOC’s collapse could have disastrous implications for marine ecosystems and biodiversity. The current system helps transport nutrients and oxygen, supporting various marine life forms along its path. If disrupted, it could lead to the decline of certain species and the disruption of fishery resources, impacting coastal communities and economies that depend on them.
Source: Yahoo News UK
The consequences may not be limited to the marine environment. The AMOC also influences the stability of the Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets. A weaker or collapsed AMOC could accelerate the melting of ice in these regions, contributing to sea-level rise and increasing the risk of coastal flooding in vulnerable areas worldwide.
While the study raises alarming prospects, it also emphasizes the importance of taking immediate action to mitigate climate change. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and implementing sustainable practices, there is hope to slow down or even prevent the potential collapse of the AMOC. International cooperation and collective efforts are necessary to address this global challenge and safeguard the delicate balance of our planet’s climate system for future generations.
A catastrophic collapse of this scale has the capability to bring about rapid and significant alterations in weather and climate patterns, not just locally but across vast regions like the United States and Europe. The consequences of such an event could be far-reaching and have profound impacts on our planet.
Source: CBS News
According to scientists, the potential collapse of the AMOC is just one of several perilous climate “tipping points” that could arise due to climate change.
According to a report from the United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change in 2019, it was forecast that the AMOC (Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation) would experience a decrease in strength during this century. However, the report also stated that a complete collapse of the AMOC before the year 2100 was improbable.