Author: Naima Syed
With ink as my medium, I traverse in the land of science and literature. The strokes of my pen illuminates with discovery and innovation in science, while it searches its origins in the depths of literature.
Water, essential for nurturing and sustaining life on earth, continues to face ill-received treatments from us due to our inappropriate actions. Now the consequence is such that the United Nations estimated a staggering two billion individuals across the globe are currently facing challenges in obtaining safe drinking water. A study published in Nature has found through simulations and predictive analysis, that towards the end of this century, around 5.5 billion people might get exposed to the polluted water. The team of researchers from the Utrecht University, Utrecht, Netherlands, conducted an analysis of surface water quality under various scenarios of…
CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) Gene-Editing tool offers numerous applications in genetic engineering ranging from plants, agriculture, to medicine and gene therapy. In a breakthrough research by the scientists at North Carolina State University, a CRISPR-based gene manipulated poplar trees were bred to achieve decreased lignin content, paving way for a sustainable generation of wood, pulp, and fiber. Led by Rodolphe Barrangou, a renowned CRISPR expert from NC State, Jack Wang, a tree geneticist, and their team employed advanced predictive modeling techniques to establish objectives aimed at reducing lignin levels. This would ultimately cut the costs of wood…
Age reversal through a novel chemical-based cocktail could be possible in future, claims a team of researchers from Harvard Medical School and conjoined efforts of institutes who participated in the study. The potion could pose high efficacy in bringing a breakthrough in the field of anti-aging gene therapy. The discovery was published in the prestigious journal Aging. David A Sinclair, lead scientist of the project explains the astonishing facts about the discovery. He elaborates that up till now, the field of anti-aging could only slow the process of senescence through gene therapy. Their findings hints at ultimate reversal of the…
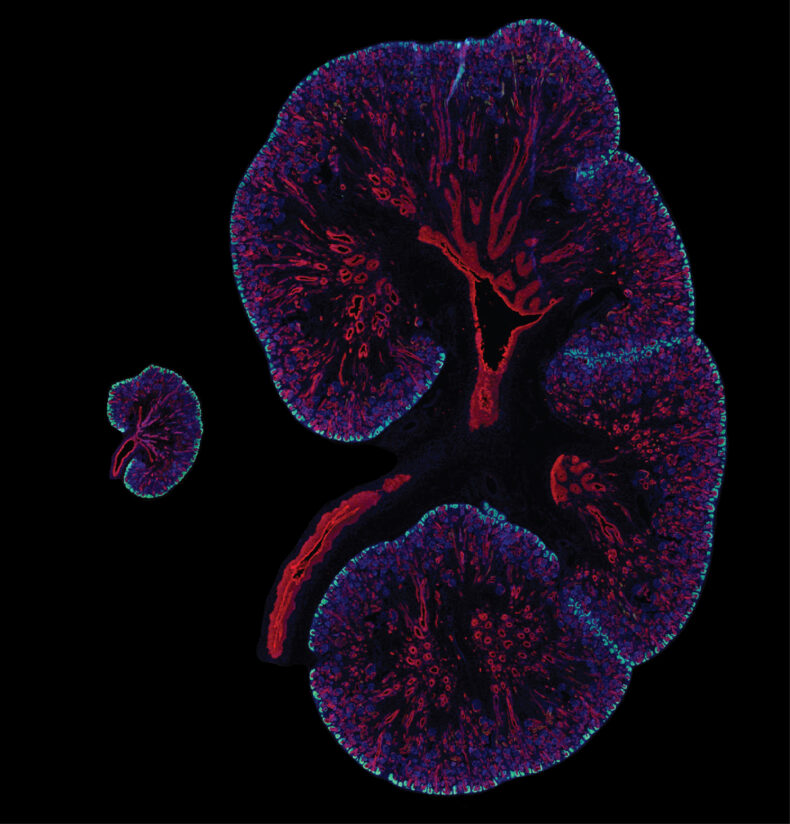
An intriguing discovery which involved rejuvenation of kidney cells was achieved by the scientists at the University of Texas. The study detailing this mechanism was published in Nature Nanotechnology. A previously unknown phenomenon of housekeeping, in which kidney cells expel out undesirable material, which helps existing cells to renew themselves and sustain longevity and health of kidneys throughout the lifetime is coming into light through this breakthrough research. While the liver and skin generate new cells through cell division, the cells in the proximal tubules of the kidney remain quiescent and do not divide. However, in cases of mild injury…
Extracted from the ocean beds, the sediments revealed valuable insights into the past in a study carried by the researchers from University of Naples Federico II, Italy and their associates. The research scientists Elda Russo Ermolli, Halinka Di Lorenzo, and team were successful in analyzing pollen from a marine core collected in the Gulf of S. Eufemia (Tyrrhenian Calabria, Italy). Their analysis enabled them to reassemble the historical shifts in territorial vegetation and land utilization spanning a period of 5,000 years. From Present to Past Analysis In a research expedition documented in The Holocene, scientists conducted core recoveries from the…
Climate sensitivity has emerged as a widespread phenomenon with profound implications on every aspect of the natural world. The impact on agriculture due its consequences on a global scale has been a worrisome issue. The second-largest global producer of wheat- India, continues to remain deeply overwhelmed by the crop’s sensitivity to the increasing levels of temperature. A study published in Nature was led by an international team of researchers including Professor Ruth DeFries from Columbia University, New York and Professor Ashwini Chhatre, from Indian School of Business, Hyderabad. Their study calculated that by the year 2040, if the agricultural practices…
Machine learning has empowered versatile domains of science, technology, industry, and e-commerce with intelligent concepts. In medical and diagnosis, it has garnered several applications that have proven to be more efficacious than traditional ones. A new study published in Nature Medicine demonstrates the same. The study led over by the researchers from the University of Pittsburgh uses electrocardiogram (ECG) readings as input to their machine learning model. The model is ultimately able to perform diagnosis of heart attacks in a rapid and reliable manner than most current approaches. At times when results from ECG are not discernible, the additional tests…
Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, imparts a greenhouse effect 25 times stronger than that of carbon dioxide per unit agricultural input. Given that methane contributes around 30% of greenhouse gas emissions in the agricultural sector, precise measurement of methane emissions from rice paddy soil holds significant importance in formulating effective climate change response policies. The Methane Evaluation Technology The widely employed approach for measuring methane emissions from rice paddy soil is the chamber method, which entails the placement of box-shaped chambers at appropriate distances on the soil. The collected methane is then quantified per unit area and time. However, this…
A protein to demystify the molecular basis of obesity has been uncovered by an international collaboration of a team of researchers from University of East Anglia, University of Cambridge, University of Pennsylvania, and Free University of Brussels. The study unfolded molecular structure of the protein UCP1 (Uncoupling Protein 1), a 33 kDa mitochondrial carrier protein, which plays a pivotal role in assisting brown fat tissue to utilize calories as heat, rather than storing calories as in white fat. This realization could offer advancement of therapies that artificially stimulate UCP1, enabling the burning of surplus fat and sugar-derived calories. A breakthrough…
The realm of space, known for its ceaseless exploration of the known and unknown, captivates and enthralls individuals all around the globe. In another expedition in the realm of space, the scientists observed a riveting object, WD0032-317B capturing their attention. This celestial body is now challenging the astronomers’ understanding, making it elusive to draw a distinction between stars and planets. This interesting object falls under the classification of ‘brown dwarf’, and possesses a myriad of extraordinary characteristics. The Space Brown Dwarfs Often called ‘protostars’, brown dwarfs are lucent, gaseous entities. The scientists refer to a conventional size range in between…
Contact us:
Copyright © 2024 Asiana Times. All Rights Reserved