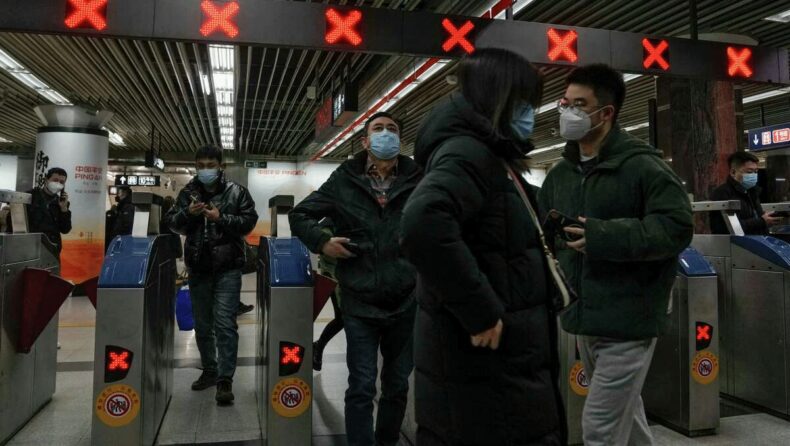
After the ease of virus contamination regulation, China faces an incremental surge in COVID-19 with high death tolls.
The National Health Commission reported that five new records of fatalities had been noticed in Beijing and that the death toll had reached 5242. The number might be lower compared to world standards, but that surge from the Zero COVID policy is dangerous.
Highlights
As a result of the anti-government protests over the stumbling economy, the government recently relaxed the strict rules of virus contamination regulation for clinical patients and funeral homes. But this step away from the “Zero-Covid” policy increases the Covid threats.
Official Report on Deaths From Covid-19 In China
According to the health authorities, only two deaths have been reported due to COVID-19 (January 30). Almost 1.9 million active cases have existed since the pandemic began. However, the case spiked in late November. Within twenty-four hours, the case reached 40,000 people infected by the new infection for the first time after the highest surge in April 2022.
However, soon the graph went down sharply. The official number of cases was 2819, which was less than the number of cases in December, with 3417 in December and 4656 in January.

But scary pictures and videos of pilled-up dead bodies and crowded hospitals have appeared on social media, though unverified. All the deaths are referred to as part of the widespread wave of new Coronavirus cases, with quotes from unnamed people spread all over social media. However, before December 19, China had not published official reports on deaths caused by COVID-19.
What Could Be The Possible Reason Of The Upsurge?
From the beginning, China used a different and strict approach to curb the growth of COVID-19 cases. The strategy may succeed to a fair degree too, but for a short span. The aggressive testing mechanism and strict regulations sparked protests in Beijing, most notably in Tiananmen Square. Some protesters also demanded the resignation of President Xi Jinping.
Due to this anti-government protest, the authorities have loosened some spheres of the restrictions, and this might explain the upsurge so far.
What Is Zero Covid Policy?
Most countries concentrated on lockdowns to curb the contamination of COVID-19. Most countries concentrated on lockdowns while allowing everyday activities to continue. However, China has followed a “zero-tolerance” policy against COVID-19 since the beginning.

Every COVID-19 patient, including the asymptomatic, was hospitalized mandatorily. Small outbreaks of the disease were controlled by executing strict lockdowns. For suspected cases and all contacts of the suspected person, quarantine or self-isolation was required. Shanghai, the financial capital of China, was entirely locked down in March to restrain the catastrophic situation.
The Drawbacks Of The Zero Covid Policy So Far
Though the zero CO2 policy showed significant success despite numerous protests, the drawbacks are agonizing. Because of the procedure, the vast majority of China’s population remained uninfected by the virus, and hence no complex immunity had developed among the population. In contrast, the fast-spreading variants of Covid managed to break the strong and rigid defense of the zero-tolerance policy, resulting in rapid growth in the Covid graph.

The same issue was observed when Omicron broke out in Hong Kong and South Korea. Every day, the death tolls in both countries affect hundreds of lives and thousands of cases. Hong Kong and South Korea protected their citizens from the virus by implementing a rigid “zero-covid” policy and aggressive testing from the early stages.
However, the vaccine is not a cure for COVID-19 disease, but rather a preventative measure. Over time, the vaccines become less effective without rapid booster doses and natural immunity.