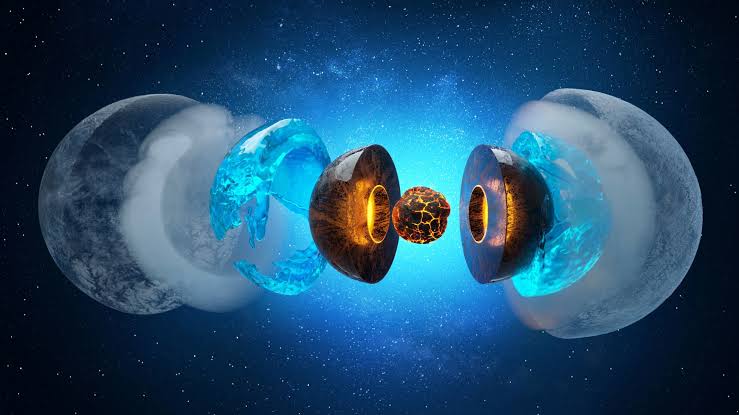
Scientists from Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois stated that they had discovered an ocean three times the volume of ALL of the world’s seas, located deep below the earth’s surface.
- Scientists have discovered a water supply three times larger than the world’s oceans.
- Water was detected between Earth’s upper and lower mantles.
- This research reveals that mantle minerals trap water molecules.These water molecules ascend again.
About 400 miles (650 kilometres) below the surface is where we can find this underground water source. Important as it may be in determining the origin of Earth’s water, this discovery is yet quite minor.
In particular, it could help us better understand the genesis of life on Earth and the oceans, and shed light on how we got here.
Backstory: Formation of the ocean

Many scientists now believe that water on Earth was brought here by comets or asteroids. As of late, this explanation has garnered the greatest backing.
This would suggest that the primordial conditions inside the solar system were far too hostile to support the presence of any form of water.
Our young sun’s intense UV radiation would strip the hydrogen from water molecules, causing them to dissociate.
Because of this, scientists have concluded that our water ice formed in the outer reaches of the solar system and was delivered to a much cooler Earth by comets or asteroids, thus providing the latter with the latter’s more nuanced chemistry.
Research at Goethe university, Frankfurt

This study demonstrates that water molecules become trapped among the minerals of mantle rock, which may be found extremely far beneath the Earth’s surface.
Prof. Frank Brenker of Goethe University’s Institute of Geosciences in Frankfurt observes that “these mineral transformations greatly hinder the movements of rock in the mantle.”
Plate tectonics pushes water to the surface.Sub-ducting plates fail to break through the transition zone, he says. This region under Europe is loaded with these plates. Deep-sea sediments are sub-ducted by slabs.
Sediments hold water and CO2.It was unknown how much water enters the transition zone as stable hydrous minerals and carbonates, and whether large amounts of water are held there.
These are favourable conditions. Wadsleyite and ringwoodite, unlike olivine at lesser levels, may hold substantial volumes of water.
In theory, the transition zone might absorb six times the water in our oceans. We knew the border layer might hold a lot of water, explains Brenker.
We didn’t know if it did. Frankfurt geoscientists’ global research gives the answer. Team examined a Botswana diamond. 660 km deep, ringwoodite dominates the transition zone and lower mantle.
Even among super-deep diamonds, this region’s gems are outstanding.
The stone contains ringwoodite. Researchers determined the stone’s chemical makeup. It resembled mantle rock shards in basalts worldwide. This proved the diamond’s mantle origin.
“In this study, we have demonstrated that the transition zone is not a dry sponge, but holds considerable quantities of water,” says Brenker.
“This also brings us one step closer to Jules Verne’s idea of an ocean inside the Earth.” Brenker says hydrous rock isn’t moist or drips water.
Research by Steve Jacobsen

Previously, it was thought that ocean water followed sub-ducting slabs and so entered the transition zone, but this study revealed otherwise. This suggests that the water cycle occurs all across the world, even the interior of our planet?
Steve Jacobsen, a geophysicist who was one of the researchers responsible for the discovery, believes that there lies evidence of a whole-Earth water cycle, which may explain the huge volume of liquid water on our habitable planet. Scientists have searched for lost deep water for decades.
Water can be found in “ringwoodite.” a blue rock. This rock is found in the Earth’s mantle, the heated layer between the planet’s surface and core.
This suggests that the newly discovered “ocean” is not blue water.Instead, water is trapped in the molecular structure of the mantle.
“The ringwoodite crystal structure, like a sponge, absorbs hydrogen and holds water.
This substance can hold a lot of water in the deep mantle.”
Jacobsen and colleagues used 2000 seismometers to study 500 earthquakes. These waves penetrate Earth.
Jacobsen: “They make the Earth ring like a bell for days afterwards,” By measuring wave speed at different depths, scientists determined which rocks the waves were going through and found ringwoodite 700 kilometres underground.
Jacobsen has proof that moist rock is under the US. Is it widespread? If so, we could learn more about Earth’s life-supporting processes.
READ MORE: https://tdznkwjt9mxt6p1p8657.cleaver.live/failure-of-the-bezos-blue-origin-rocket/