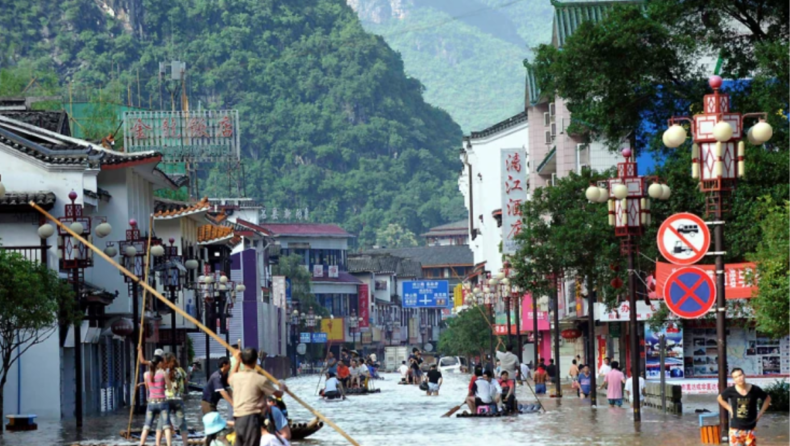
Flooding has forced the evacuation of tens of thousands of residents in southern China, and more rain is predicted.
Chinese authorities issued the year’s first red alert, the most severe warning, for potential mountain torrents on Sunday.
There is forecasts of increasing sea levels and the possibility of landslides. The manufacturing powerhouse of Guangdong closes its schools, offices, and public transportation.
Firstly, nearly 5,000 individuals in the neighboring province of Jiangxi have had their lives disrupted. Secondly, their houses damaged badly.
Moreover, in Guangdong, mostly in the cities of Shaoguan, Heyuan, and Meizhou, about the same number of people have been impacted.
Heavy rain is forecasted
More rain is expected over the next few days. The recent torrential rains have destroyed crops, automobiles, residences. Even some city roadways. The first red alert of the year—the strongest warning—was issued by Chinese officials on Sunday for potential mountain torrents.
However, rescue teams on inflatable boats rescued people stuck in their houses in flooded villages in Zhejiang Province, a bit farther north.
For instance, the central and southern regions of China typically receive the greatest rainfall. These are the ones that experience floods the most frequently throughout the summer.
In some locations, this year’s floods are the worst in decades. It comes on top of the severe COVID-19 laws. It made it difficult for people to travel, find work, and go about their daily lives.
Investments on dams
The Yangtze River is China’s most powerful river. It was the site of one of the country’s greatest floods in recent memory. Moreover, it claimed more than 2,000 lives. The river has ruined almost 3 million dwellings.
However, the government has made significant investments in hydropower and flood control projects, such as the enormous Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze.
As a result of climate change, tropical storms are becoming more powerful globally. It increases the flooding that endangers people’s lives. It also endangers agricultural production, and groundwater.