The border issue between Beijing and Thimphu is almost over, according to Bhutan’s prime minister, and there have been no Chinese intrusions into its territory. The relationship between India and Bhutan is particularly unique, yet China is still the room’s dragon.

Last week, during the three-day visit of Bhutan’s King Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck to New Delhi, the two sides attempted to diffuse the uproar in that nation over the Prime Minister of Bhutan’s comments regarding border discussions with China.
The contentious border issue was not mentioned in an extensive joint statement. The statement’s final sentence, however, stated that “His Majesty’s visit also gave a chance for both nations to evaluate the full range of bilateral cooperation and to advance our strong bilateral friendship.”
For many years, Bhutan and India have maintained a strong friendship. The latest discussion between the two nations was centred over the ongoing border talks between China and Bhutan. The gathering emphasised the close ties between the two nations and their shared determination to elevate ties between India and Bhutan. Both nations benefit from this alliance, which also has regional geopolitical ramifications.
Bhutan has had a positive relationship with India ever since it gained its independence in 1947. Bhutan’s largest commercial partner, India, offers it a lot of financial and technical support.
What changes have there been in India and Bhutan’s ties recently?

Standby credit facility: India has offered Bhutan an additional “standby” credit facility at its request, in addition to the two standby credit facilities currently in place between the two nations.
India has agreed to take Bhutan’s request into account regarding the sale of power from its Basochhu hydroelectric project, which could be accomplished through the market’s energy exchange mechanism. Bhutan has requested that India take this request into account regarding the sale of power from Bhutan’s Basochhu hydroelectric project.
India is concentrating on making a viable, long-term agreement for the export of agricultural products from Bhutan. Outside of hydropower projects, they also intend to broaden their collaboration in the energy sector. Moreover, India wants to establish a long-term bilateral agreement to guarantee Bhutan a consistent supply of essential goods. These products include coal, fertilisers, and petroleum.
Economic Support: India is Bhutan’s major commercial partner and an important source of financial assistance. For instance, India’s trade with Bhutan has increased by over three times since 2014, from US$484 million in 2014–15 to US$1.42 billion in 2021–22, making up about 80% of Bhutan’s total trade.
Security: India has been essential in maintaining Bhutan’s security. For instance, India’s military assists Bhutan in securing its borders, and India has assisted Bhutan in fending off rebel organisations.
Assistance on the diplomatic front: India has been Bhutan’s most steadfast ally. India has supported Bhutan in its diplomatic efforts and has been crucial in preserving Bhutan’s sovereignty.
India has been offering aid to Bhutan’s socioeconomic development since the early 1960s. This assistance has taken the form of direct budgetary support, multi-sectoral project-tied assistance, and minor development programmes.
Bhutan’s Significance to India
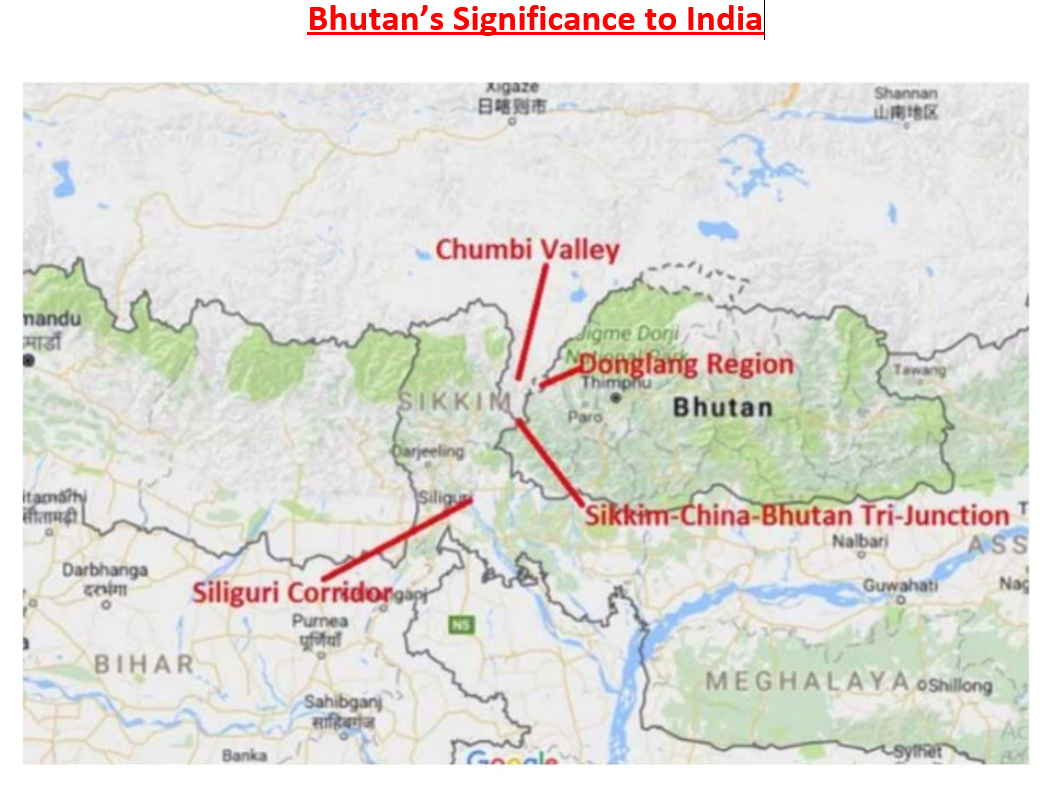
Strategic importance: For India, Bhutan is of crucial strategic importance. Bhutan and China have the same boundaries, and Bhutan is seen by India as a buffer state between the two countries. For instance, China has been making significant concessions in the north for years in exchange for a considerably smaller region in Doklam. Bhutan has always rejected this offer because it recognises India’s security concerns and would not establish its border with China without taking India’s interests into consideration.
Strategic Partner: Bhutan is an important regional ally for India and offers security guarantees to its northeastern regions.
Cultural Relations: Deep cultural relations exist between Bhutan and India. India’s culture has had a significant impact on the religion, language, and customs of Bhutan. Bhutan has also been a steadfast advocate for India’s cultural diplomacy.
Hydropower collaboration: The foundation of bilateral economic cooperation is mutually beneficial hydropower cooperation with Bhutan, which offers India clean power and economic development for Bhutan. Bhutan now has the greatest per capita GDP in South Asia because of the growth of hydroelectricity as one of its main sources of income.
What changes have recently occurred in China’s and Bhutan’s relations?

Recent Changes in Connections Between China and Bhutan:
Border Conflict: There is a long-standing border conflict between China and Bhutan. Bhutan and China both claim the Doklam plateau as part of their respective territories. The Doklam plateau region saw a military confrontation between the two nations in 2017, which was eventually resolved after many weeks of difficult discussions.
Economic Ties: China and Bhutan have been collaborating economically, especially in the fields of infrastructure development, agriculture, and tourism. An agreement to create a sister city connection between Thimphu, the capital of Bhutan, and Xining, the capital of China’s Qinghai province, was signed by the two nations in 2020.
People-to-People Relations: In recent years, there has been a rise in the number of Chinese tourists travelling to Bhutan as well as Bhutanese students studying in China. The two nations struck a deal in 2019 to foster tourist cooperation.
COVID-19 Pandemic: China has sent Bhutan equipment and medical supplies to aid in the fight against the COVID-19 epidemic. China donated COVID-19 vaccinations to Bhutan in 2021, and the vaccines were used to immunise Bhutanese inhabitants.
Diplomatic Relations: Bhutan has historically been circumspect in its dealings with China and has close ties to India. Bhutan has attempted to strengthen ties with China in recent years, and in 2021, the two nations commemorated the 20th anniversary of the start of diplomatic ties.
What effects do China-Bhutan relations have on India?
Strategic repercussions: India’s security and strategic objectives may be threatened by China’s growing sway in Bhutan. By surrounding India from all sides, it may offer China a tactical edge in the area.
Border implications: India has reservations about Bhutan’s border with China. The security of India’s border may be adversely impacted by territorial conflicts between Bhutan and China if Beijing expands its influence in Bhutan.
Economic implications: India’s commercial and economic interests in the area may be harmed by China’s expanding economic influence in Bhutan. Moreover, it may result in China obtaining access to Bhutan’s natural resources, which would put India’s energy security at risk.
Regional repercussions: The balance of power in the area may change as a result of China’s growing influence in Bhutan. It may cause a change in the balance of power in the area and have an effect on India’s standing there.
Diplomatic repercussions: Bhutan’s long-standing pro-India foreign policy may be affected by China’s expanding influence there. This would cause Bhutan to turn away from India and ally more with China, which might have diplomatic repercussions for India in the area.
What should be done to advance ties between India and Bhutan?
Improving Economic Relations: Through fostering bilateral trade and investments in several industries, India and Bhutan may collaborate to improve economic cooperation. Bhutan may benefit from India’s technological know-how in strengthening its infrastructure, tourist sector, and hydropower projects. Joint ventures, the creation of industries, and the signing of free trade agreements can all help achieve this.
Address China’s concerns: India might make an effort to allay some of China’s worries about its presence in the area by encouraging openness and communication in its interactions with Bhutan and other nearby nations.
Border Issues: India and Bhutan should cooperate to find a peaceful solution to their disputes over the border. This will support keeping the border calm and improve mutual trust and confidence between the two nations.
Use multilateral forums: India may engage China on regional concerns and seek to find amenable solutions by using multilateral forums like the BRICS and the SCO.
Enhancing Connectivity: By offering improved road and rail connections, India can assist Bhutan in enhancing its connectivity. The two countries trade and tourism will increase as a result of this.
Improving Military Cooperation: By holding more frequent combined military drills and training sessions, India and Bhutan may seek to improve their defence cooperation. Bhutan will be able to strengthen its defensive capabilities due to this.
Handling Environmental Concerns: Through exchanging sustainable development knowledge and experience, India and Bhutan can work together to address environmental concerns. Bhutan’s worries about climate change and natural catastrophes may also be addressed with India’s assistance.
Enhancing Interpersonal Contact: There should be more student, intellectual, and cultural group exchanges between India and Bhutan in order to develop cultural ties between the two nations. This will aid in fostering mutual respect and understanding between the two nations.













