Table of Contents
With the help of the very sophisticated, advanced instruments onboard NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, scientists have gathered data regarding the climatic conditions of a planet Orbiting outside the Solar System.
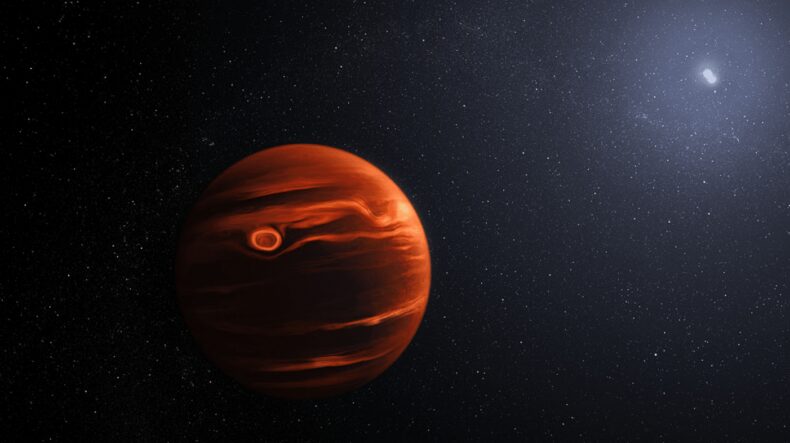
The Planet targeted by the James Webb telescope is an exoplanet (a planet outside the solar system) called VHS 1256 b, scientists explained in a recent press release that it is a massive brown dwarf planet that orbits not one but two stars with a period of 10,000 years and is 40 light years away. Scientists say that the exoplanet VHS 1256 b orbits 4 times farther than that of how far Pluto orbits the Sun.

Image Credits: webbtelescope.org
The fact that this planet orbits 4 times far than that of how far Pluto orbits the sun makes this planet a prime target for Webb to study its atmosphere because the light from its host star doesn’t get mixed up with the light from VHS 1256 b, which allows Webb to make accurate observations of the planet’s climatic conditions.
According to the press release, Webb made observations that the temperature in the higher altitudes of the exoplanet VHS 1256 b’s atmosphere reaches around 1500 degrees Fahrenheit. And in those clouds, Webb detected that there were both large and small grains of Silica dust, the small grains are comparable to the particles in the smoke dust and the large ones are comparable to very extremely hot grains of sand.
Nasa Report On Dust Storm
The press release also mentions that clear detections of water, methane, and carbon monoxide were made from Webb’s data by a team led by Brittany Miles from the University of Arizona. They also found evidence of carbon dioxide in the data gathered.
Compared to Earth the exoplanet VHS 1256 b has a much lower gravity allowing the clouds to hover at higher altitudes giving an advantage to the James Webb space telescope to make clear and precise observations. The exoplanet was discovered in 2015 by Vista Telescope in Chile and received the nickname ‘Super Jupiter’ due to its similarities with Jupiter but has a mass 12 to 18 times the mass of Jupiter. Early research conducted on this exoplanet yielded that this planet has dust present in its atmosphere but the observations made by Webb confirmed those early studies made on VHS 1256 b.
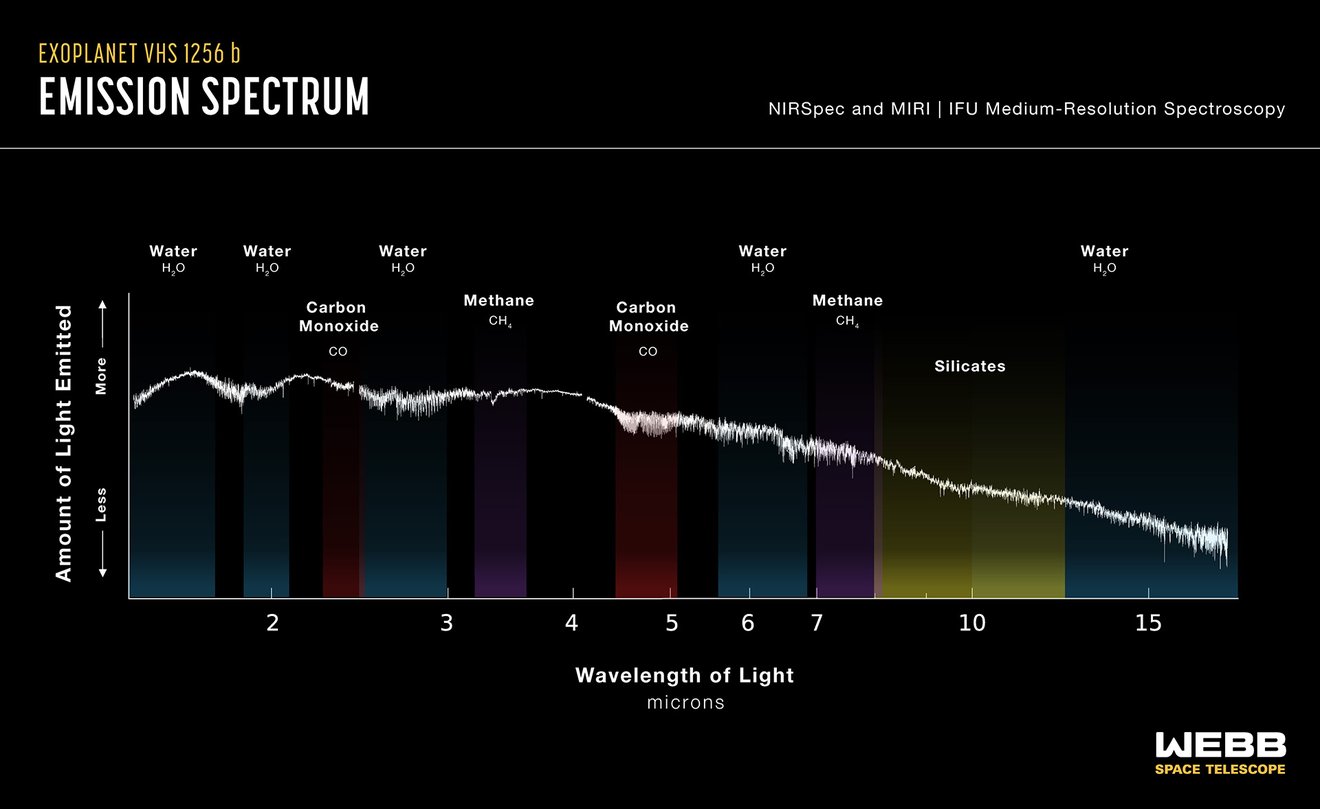
These conclusions were made using data gathered from two very sophisticated instruments namely MIRI and NIRSpec onboard the Webb telescope. Since VHS 1256 b orbits very far away from its host star direct observations were made rather than using techniques like Coronagraph and the Transit Technique to make observations on the planet’s atmosphere and gather data.
Ben Biller, Co-Author of the study from the University of Edinburgh in Scotland said that due to exceptionally less time that is needed to make observations by the Webb telescope, researchers felt that they have mountains of data to sift through that can make so many additional discoveries.

James Webb Space Telescope is a very complex and advanced telescope that was made to look back to and understand the early stages of the universe and study exoplanet’s atmospheres and find out whether they are suitable to host life. After it started making observations it made such tremendous discoveries and we are just getting started.













