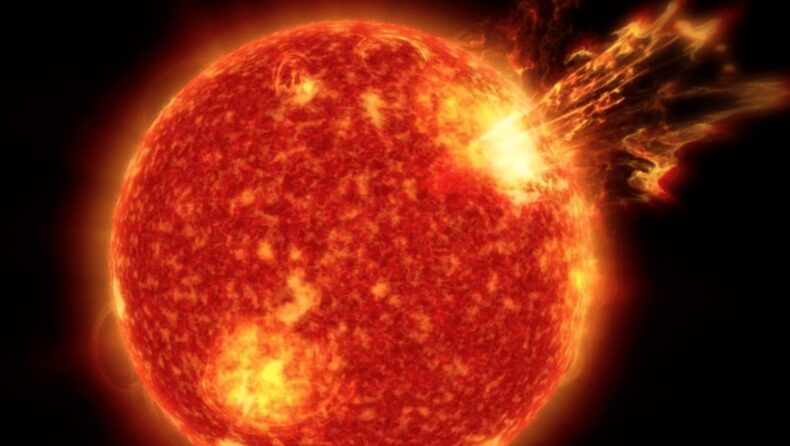
Experts warned that the explosion’s debris could be headed for Earth. Solar flares are intense energy bursts that can disrupt radio transmission. The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) of NASA obtains multiple-wavelength photographs of the Sun

Observatories have detected a 200,000-kilometre-long filament eruption from the Sun after it exploded in a cannibalistic eruption. The lengthy strand of magnetism emerged like a rubber band from the southern hemisphere of the Sun.
The SOHO observatories have detected a Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) emanating from the explosion location, which was predicted by experts to be headed toward Earth. However, Spaceweather.com stated that the data stream ceased before the entire CME was seen.
AR3112, a massive sunspot that has been unstable, is on the verge of exploding, with a 65% likelihood of an M-class flare and a 30% possibility of X-class flares erupting from the region. The explosion may be directed directly towards the planet and may be geoeffective.
More than a dozen black cores are dispersed across 1,300,000 kilometres of the sunspot’s surface.

While solar flares are powerful energy bursts that can disrupt radio communications, electric power grids, and navigation signals and pose risks to spacecraft and astronauts, a geomagnetic storm is a major disturbance of Earth’s magnetosphere that occurs when there is a highly efficient exchange of energy between the solar wind and Earth’s space environment.
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) obtains multiple-wavelength photographs of the Sun to aid in the study of its characteristics and activities.
As the Sun reaches the height of its solar cycle, activity is expected to increase with the emergence of new sunspots that could launch catastrophic explosions toward the inner solar system.
The Cannibal CME eruption that occurred on the Sun early on Tuesday morning landed on Earth in bits. Solar wind data from the third and fourth of October, as reported by Spaceweather.com, appear to show indicators of a large number of CMEs. It did result in a series of intense auroras being visible above the surface of the earth.