Table of Contents
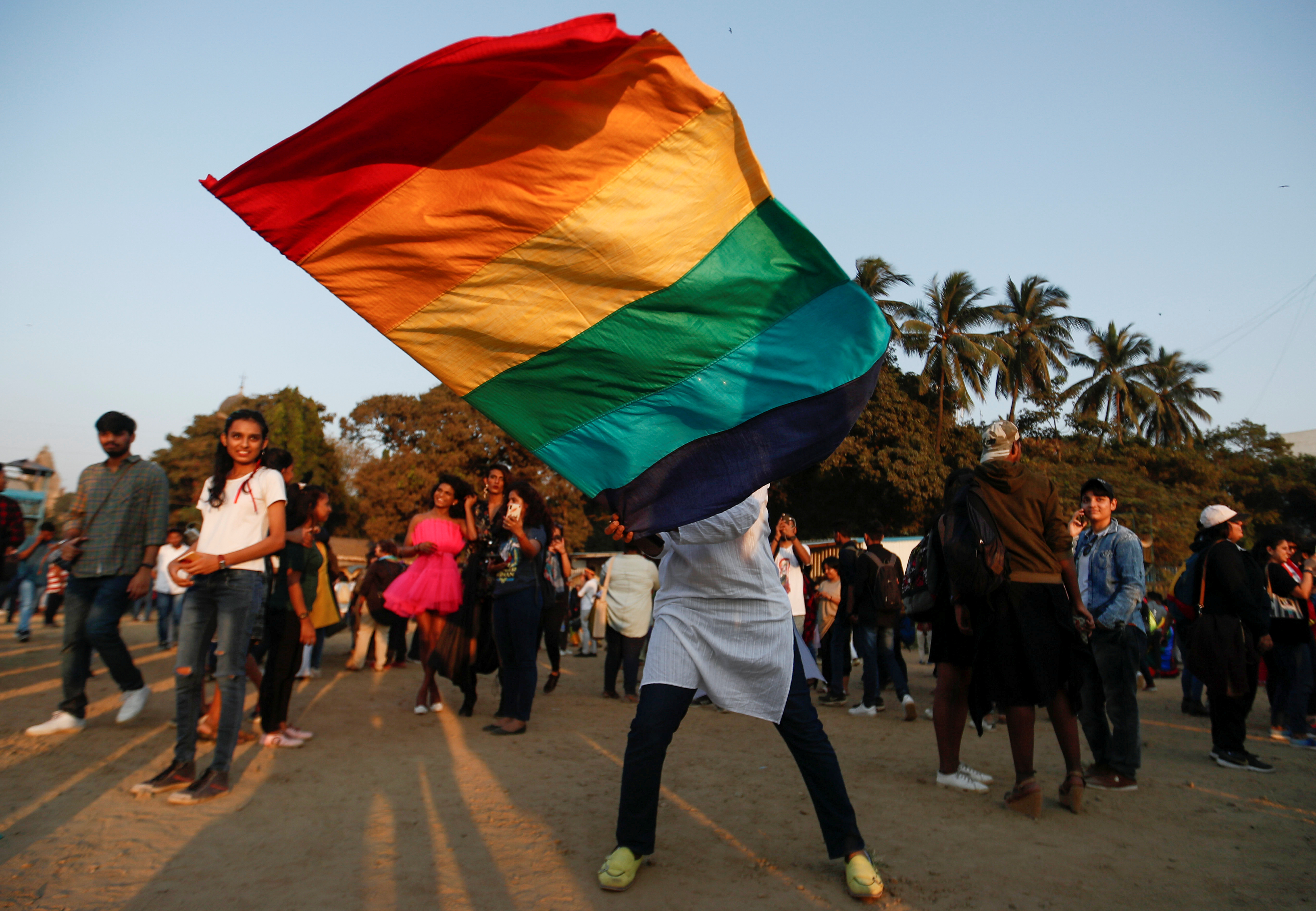
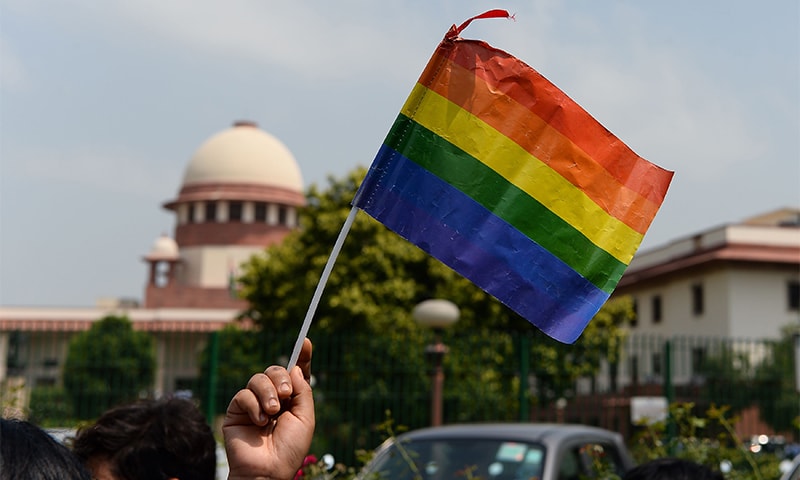
Same-sex marriage has been a contentious issue in India for several years, with both supporters and opponents fiercely debating the legal and social implications of granting same-sex couples the right to marry. While progress has been made through judicial recognition, legislative power remains a crucial factor in determining the legal sanctity of same sex marriage in India. In this blog post, we’ll explore the ongoing debate over same-sex marriage and examine the roles played by both the judiciary and legislature in its recognition. Join us as we delve into this complex topic that affects not only urban elitists but also every member of Indian society who values equality and maintainability under the law.
LGBTQ+ Community in India
The debate over same-sex marriage in India has been a hotly contested issue for several years. While some argue that it is a matter of individual rights and equality, others maintain that the sanctity of traditional marriages should not be tampered with.
Urban elitists have often led the charge for recognition of same-sex marriages, citing examples from other countries where such unions are legal. However, opponents argue that India’s cultural values and traditions must be preserved at all costs.

The LGBTQ+ community in India has made significant strides towards achieving their goal of legalized same-sex marriage. In 2018, the Indian Supreme Court struck down Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code which criminalized homosexuality. This ruling was seen as a major victory by supporters of LGBTQ+ rights.
However, despite this landmark decision by the judiciary, same-sex marriage remains unrecognized by law in India. It is now up to the legislature to decide whether or not to take action on this issue.
The debate over same-sex marriage in India highlights larger issues surrounding individual liberties and societal norms. As society continues to evolve and progress towards greater acceptance and inclusivity, it will be interesting to see how this particular debate unfolds in the coming years.
The Role of the Judiciary in same-sex marriage Recognition
In India, the judiciary has played a crucial role in recognizing the rights of LGBTQ+ individuals. The landmark judgment of Navtej Singh Johar v. Union of India by the Indian Supreme Court decriminalized homosexuality and recognized that LGBTQ+ individuals have equal rights under the law.
However, when it comes to same-sex marriage recognition, the role of the judiciary is limited. The Indian Constitution does not explicitly recognize same-sex marriage as a fundamental right, leaving it up to interpretation by judges on a case-by-case basis.
In recent years, there have been several cases filed before various high courts seeking recognition for same sex marriages. While some courts have granted relief to petitioners, others have dismissed such petitions citing lack of legislative sanction.
The judiciary’s role in same-sex marriage recognition is restricted because ultimately it is up to the legislature to pass laws recognizing such marriages. However, given that progress towards legislative reform has been slow-moving and fraught with opposition from certain groups and parties (such as urban elitists), judicial intervention may be necessary in securing legal sanctity for same-sex marriages.
While limited in its power when it comes specifically to same-sex marriage recognition, the Indian judiciary has played an instrumental role in advancing LGBTQ+ rights more broadly through its historic judgments and interpretations of constitutional protections against discrimination based on sexual orientation or gender identity/maintainability.

The role of the legislature in same-sex marriage recognition
The legislature plays a crucial role in the recognition of same-sex marriages. In India, marriage is considered a legal and social institution that has been defined by the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955 for Hindus and other religions have their own personal laws. However, there is no law governing same-sex marriages as it is not recognized under Indian law.
The Indian Parliament has the power to make laws on any subject under its jurisdiction, including marriage. The legislators have the authority to pass or reject any bill related to same sex marriage recognition. In 2019, MP Supriya Sule introduced a private member’s bill in Lok Sabha seeking legalization of gay marriages but it was defeated with just 24 votes in favour.
Apart from introducing bills related to same-sex marriage recognition, legislators also play an important role in creating awareness about LGBT rights among people through their speeches and statements made at various forums like parliament debates and rallies.
It is essential for lawmakers to understand that recognizing same-sex marriages will help combat discrimination against LGBTQ+ community members who currently face societal stigma due to their sexual orientation. Thus, it becomes imperative for them to work towards making policies more inclusive regardless of one’s gender identity or sexual orientation.
While judiciary can interpret constitutional provisions broadly enough to include same-sex couples’ right of equality & life; but ultimately legislative action recognising such unions remains necessary as state-sanctioned legal sanctity will allow individuals equal access & protection under the law without relying solely on court cases which may be susceptible over time according to changing political winds or judges interpretation tendencies especially where urban elitists are disproportionately represented within higher echelons government bureaucracy leading towards lack maintainability.
This debate highlights not just differing opinions on same sex marriage but also broader issues around democracy and representation. It remains crucial that all voices are heard equally as we work towards building a more inclusive society for everyone.
Read More: DCPCR Moves SC Supporting Legalisation of Same-Sex Marriages













