In the solar system, a disk-shaped structure of dust particles and gas rotates around the sun.
A new study of the previous meteorites by the researchers and scientists at MIT and other places said a mysterious gap was present within this disk. This incident occurred about 4500 billion years ago, and this took place at home near the asteroid belt where it is presently.
The analysis, which the researchers and scientists make, was published in Science Advances. These published articles provide direct evidence about this gap.
Benjamin Weiss’s statement:
“Over the last decades observations have shown that cavities, gaps, and rings are common in disks around other young stars,” said Benjamin Weiss. He is a professor of the planetary sciences in MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (EAPS).
These are important but poorly understood signatures of the physical processes by which gas and dust transform into structures. Likewise, the cause of such a gap in the solar system is still now a mystery. One of the possibilities for this is that asteroids may have been an influence.
As the giant gas took shape, the tremendous gravitational pull could have pushed dust particles and the gases towards the outskirts. This further left behind a gap in the disk that was developing.
Another explanation is related to these winds. These are the winds that are emerging from the surface of the disks. Strong magnetic fields govern every system.
The gas giants:
When these magnetic fields interact with a rotating disk of gas and dust particles, it can produce winds which is several times strong enough to blow the materials out. This leaves behind a gap in the disk. Regardless of its origins, gas in the solar system likely served as a cosmic boundary.
It keeps all the materials on either side of it to keep interacting with the gases. This physical structure could have shaped the composition of the solar system. For instance, the dust particles and gases are considered terrestrial bodies on the inner side of the gap.
While on the other hand, the dust particles and the various forms of gases are relegated to the farthest side of the opening formed in the icier regions as the neighbouring gas giants.
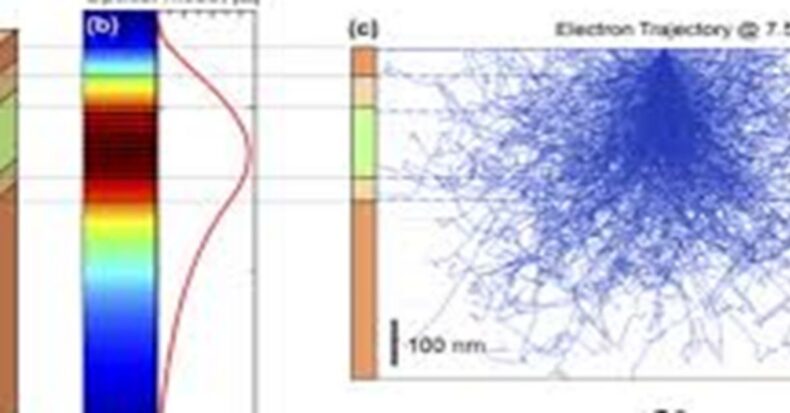
The analysis made by Weiss found the meteorites for signs of a magnetic field. The strength and direction of this magnetic field can be changed depending on the various processes within the disk. These rocks are found to have originated in any reservoir or in any of the regions where these structures existed.
Isotropic structures:
“It’s quite hard to cross this gap, and a gaseous structure would need a lot of extreme torque and momentum. So, this gives significant evidence that the formation of the gaseous structures was restricted to specific regions in the solar system. Over the last decades, scientists and researchers have observed an important split in the composition of meteorites.
These meteorites have rotated on the solar system. These space rocks have been formed at different times originally, at various locations while in the solar system. Those that have been analysed exhibit one of the two isotope constitutions.
It is hard to find that the meteorites have been found to exhibit both. This is a conundrum. It is known as the “isotropic dichotomy“. Scientists and researchers have found that this dichotomy may be the result of a gap in the disks of the solar systems.
However, the presence of such a gap does not have any evidence,” said Cau Borlina. He is the lead author of EAPS. Weiss is the co-author of this research.