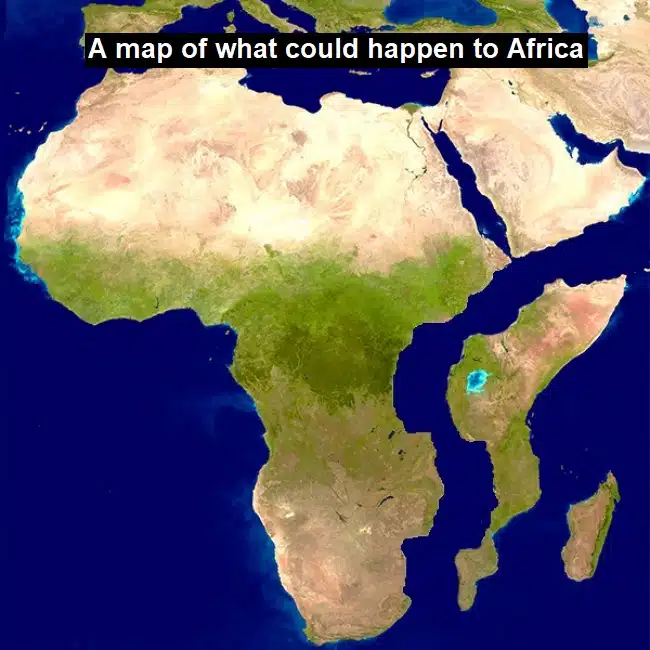
Scientists have revealed that the African continent could eventually split into two parts, resulting in the creation of a new ocean. The East African Rift, a 35-mile-long crack in Ethiopia’s deserts, marked the beginning of this process in 2005. Researchers believe that the rift could eventually become an oceanic rift, similar to those that created the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden between East Africa and Western Asia.

Crack On Africa’s Border
The crack was found to be at the border of three tectonic plates that have already been distancing themselves for some time: African Nubian, African Somali, and Arabian. GPS tracking has shown that land movements between these plates have been continuously occurring at different rates, with the Arabian plate moving away from Africa at a pace of one inch per year.
The creation of a new ocean would have significant implications for the African continent, including the potential for landlocked countries to gain coastlines. Uganda and Zambia, for example, could eventually have their own coastlines in future. This would bring significant economic benefits, such as increased access to international trade and tourism.
The East African Rift also has a rich cultural history. It is home to several indigenous communities, including the Maasai people, who have lived in the region for centuries. The Maasai are known for their traditional way of life, which includes pastoralism and a close relationship with the natural world.
Border Split In Africa

However, the region is also facing several challenges. The rapid expansion of human settlements and agriculture is putting pressure on the unique ecosystems of the East African Rift. Climate change is also contributing to the degradation of the region’s natural resources, including water and soil.
Christopher Moore, a doctorate student at the University of Leeds, said, “This is the only place on Earth where you can study how a continental rift becomes an oceanic rift.” The process is expected to occur over millions of years, so it is unlikely that any of us will witness the creation of this new ocean. However, scientists are excited about the possibility of studying this unique geological process.
Ken Macdonald, a marine geophysicist and professor emeritus at the University of California, commented, “As we get more and more measurements for GPS, we can get a much greater sense of what’s actually happening.” This technology will be vital in monitoring the displacement of the tectonic plates and predicting the potential formation of the new ocean.
While the creation of a new ocean is still in the distant future, it is important to consider the potential implications for the African continent. The splitting of the continent would result in significant changes to the landscape and could have a profound impact on the lives of those living in the affected regions. However, it could also bring opportunities for economic growth and development.

It is important to note that this geographical change is not an immediate threat, and there is no need for panic. Scientists are simply observing and studying the natural process of the Earth’s crust moving and shifting. However, it is important to continue monitoring these changes to better understand the geological processes that shape our planet.
The topographical change in Africa is an exciting prospect for scientists studying the Earth’s geological processes. While the process is expected to occur over millions of years, it could eventually result in landlocked countries gaining coastlines and significant economic benefits. It is important to continue monitoring these changes and studying the unique geological processes taking place in East Africa.
ALSO READ: Is the end near for the Crown in 21st century?