DSN is NASA’s international range of giant radio antennas that aids interplanetary spacecraft missions. It is upgrading to make communication with more spacecraft than ever so and ever such. In addition, to accommodate evolving mission needs.
About DSN
The NASA Deep Space Network or DSN is a worldwide network of American spacecraft communication ground segment facilities, which is in the U.S. (California), Spain (Madrid), and Australia (Canberra).
It is NASA’s international range of giant radio antennas that aids interplanetary spacecraft missions.
In addition to a few that orbit Earth. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory or JPL conducts the DSN. It operates many of the agency’s interplanetary robotic space missions as well.
History
The pioneer of the DSN set up in January 1958. NASA officially launched on October 1, 1958. For consolidating the separately developing space-exploration programs of the U.S. Army, U.S. Navy, and U.S. Air Force into one civilian institution.
Current Mission
The DSN is upgrading to make effective communication with more spacecraft than ever and accommodate evolving mission requirements.
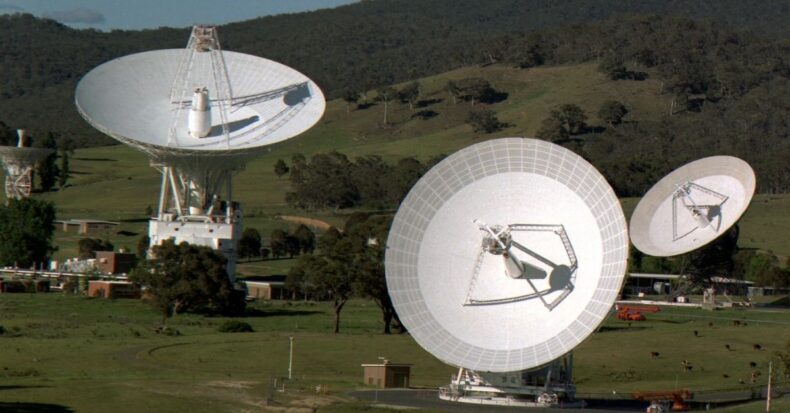
The 70-meter Deep Space Station 14 is a giant DSN antenna at the Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex near Barstow, California.
When NASA’s Mars 2020 persistence rover arrived on the Red Planet, the agency’s DSN was there, enabling the mission to exchange the data that assisted make the event come true.
When OSIRIS-Rex took asteroid Bennu’s trials the last year, the DSN served a significant role by sending the command sequence to the probe to transmitting its stunning images back to Earth.
The network is the pillar of NASA’s DSN since 1963. It is supporting 39 missions regularly, with over 30 NASA missions in upliftment.
The team behind it is currently working to enhance capacity, making an ample number of up-gradation to the network; that will help out the upcoming space exploration.
The DSN permits missions to track, send commands, and receive scientific data from faraway spacecraft.
The network consists of tracking antennas throughout three complexes spaced worldwide- the Goldstone complex near Barstow, California; in Madrid, Spain; and Canberra, Australia.
Upgradation of Network
In January 2021, the DSN greeted its 13th number dish. It is named Deep Space Station 56 (DSS-56). This latest 34-meter-wide dish in Madrid is an “all-in-one” antenna. Previous antennas bound in the frequency bands.
They can receive and transmit, often create restrictions on them to communicate with specific spacecraft. DSS-56 was the first dish to use the DSN’s full extent of communication frequencies as early as it went online and share with all the missions supported by DSN.
Shortly afterwards, escorting DSS-56 online, the DSN team did 11 months of complex upgrades to Deep Space Station 43, the massive 70-meter antenna in Canberra.
DSS-43 is the very dish in the Southern Hemisphere with a highly powerful transmitter that broadcasts the correct frequency. DSS-43 will serve the network for decades to come with rebuilt transmitters and developed facilities features.
New Approaches
The network is also keeping its eye on recent approaches to how it goes about its work. Like, for most of the DSN’s history, each complex conduct locally.
Currently, with a protocol called “Follow the Sun,” each complex takes movements running the whole network in the period of their day shift and then hands off control to the upcoming complex at ending of the day in that region.
Essentially, a global relay race that takes place every 24 hours. Future missions can also set up other types of communications.
Such as, NASA tested optical laser line-of-sight communications on the LADEE lunar orbiter mission in 2014. Now it is planning various additional tasks to test infrared laser relays.
Oft, the first indication we get that a Mars lander is active and satisfactory is from the DSN, which people can follow up live online.
It’s a pleasure to look at the iconic large DSN dishes that assisted Apollo crews to the Moon and back carry-on guiding spacecraft, rovers, and finally humans through the solar system.