Broadening biosphere reserves across the world, mainly in Asia, will enable millions of people to understand a decent fortune, one that is in unity with nature. November 3 will be the first International Day for Biosphere Reserves, to be commemorated at the beginning of 2022.
About World Network of Biosphere Reserves
The World Network of Biosphere Reserves of the MAB Programmed consists of a dynamic and interactive network of sites of excellence. It enables the balanced integration of people and nature for sustainable advancement through participatory dialogue; understanding sharing; poverty decrease and human well-being modifications; respect for cultural significance and society’s capacity to cope with modification – thus participating in the 2030 Agenda and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Accordingly, the Network is one of the main worldwide tools to create and implement sustainable advancement in a broad array of contexts.
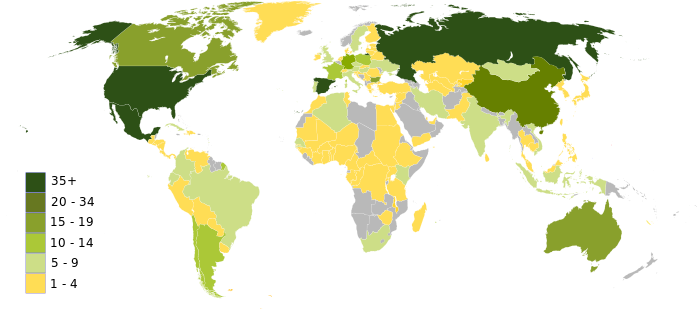
The World Network of Biosphere Reserves stimulates North-South and South-South collaboration and depicts a different tool for worldwide cooperation through sharing proficiency, trading experiences, building ability, and promoting the best methods. There are 738 biosphere reserves in 134 nations, comprising 22 transboundary sites.
About Biosphere Reserves:
Biosphere reserves are places where humans live in symmetry with nature, and where there is a beneficial hodgepodge of sustainable advancement and nature preservation. Biosphere reserves are regions of terrestrial and coastal/ marine ecosystems where both flora and fauna are conserved. They are Science for Sustainability assistance areas. – stimulating analysis in ecological preservation and environmental preservation.
The theory of Biosphere Reserves was introduced in 1971 as a part of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)’s ‘Man and Biosphere (MAB) Program.
An optimistic platform to the network (WNBR):
The WNBR, a system of sites of greatness, is a different tool for coalition through sharing understanding, trading experiences, building ability, and stimulating decent exercises. It is of considerable significance because the ecological carrying capacity of the planet earth has been overrun. We have to revert to living in symmetry with nature — to inhale and exhale clean air again, have access to sufficient good water, eat healthy and cheap food, and live in prestige.
Possibilities in South Asia
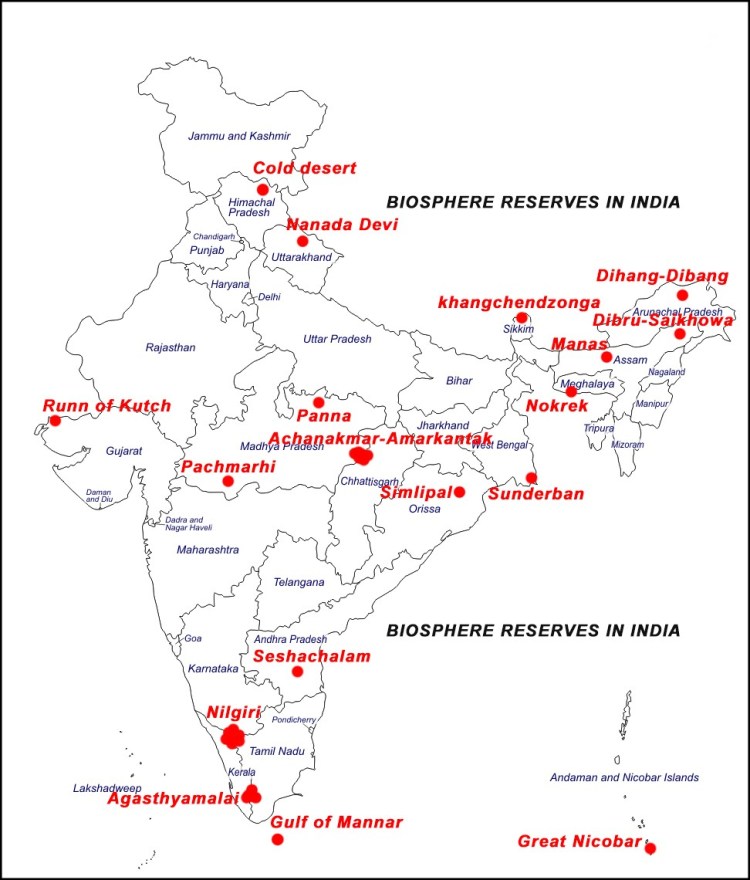
In South Asia, over 30 biosphere reserves have been found. The first one was the Hurulu Biosphere Reserve, in Sri Lanka, and in India, the first was the Nilgiris (2000) stretching over Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala. India is a vast sub-continent, an arising superpower of infinite chances. It has become a crucial universal player in environmental sustainability problems. India is likely to evolve into the world’s most populated country in 2024.
Spain, with a landmass of 506,000 sq km, and a population of 47 million is one of the overseeing contributing WNBR nations globally, with 53 properties. In comparison, India, with a region of 3.3 million sq km, and a community of 1.4 billion, can expand more biosphere reserves, with an emphasis on the seven sisters in north-east India.
Biosphere reserves have all created science-based supervision proposals, where local explanations for sustainable human living and nature conservation are being examined, and decent methods applied. Problems of worry comprise biodiversity, clean energy, atmosphere, environmental education, and water and waste supervision, supported by scientific analysis and monitoring.
All biosphere reserves are internationally comprehended areas on land, at the coast, or in the blues. Governments alone determine which regions to assign. There is a lack of know-how and economic resources. With help from the richer countries and the private sector, it would be preferable to improve more biosphere reserves.
Gist
Bangladesh, Bhutan, and Nepal are on the preference list of UNESCO for its Biosphere Reserve policy. The existence of the new World Network of Mountain Biosphere Reserves gives a welcome chance for Bhutan and Nepal to establish their first biosphere reserves and participate in the national network. If these pockets of wish can broaden, with at least one biosphere reserve per nation in Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal until 2025 (with extra biosphere reserves in India’s North-East and along the coasts) it will bestow satisfaction to millions of people that a decent fortune is possible — one where we will live in symmetry with nature.













