Upcoming gene medicine for blood disorders. A new group of medications for cystic fibrosis. Increased access to telemedicine. According to an esteemed panel of clinicians and researchers, these innovations will enhance healing and change healthcare in the coming years.
About Bubble CPAP:
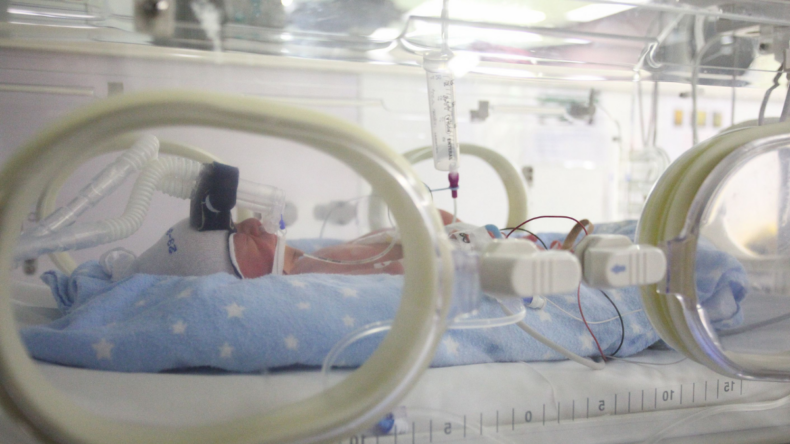
Bubble CPAP for increased lung function is often seen in many premature babies. Underweight and frail babies are born prematurely often require specialized care, including ventilation for infant respiratory disorder syndrome (IRDS).
For IRDS, infants have commonly affected surfactants during mechanical ventilation, a practice that can cause as many as the lasting lung injury in many preterm infants and contribute to the development of chronic lung disease in infants.
Unlike the process of mechanical ventilation, b-CPAP is a non-invasive ventilation strategy – delivering continuous positive airway pressure to newborns to maintain lung volume during exhalation.
The oscillating rather than constant pressure plays a role in its safety and efficacy, minimizing physical trauma and stimulating lung growth when administered over a prolonged period.
Covid on infants:
Covid saw an increased rate of telemedical treatment as clinicians needed to conduct the patient had visits online.
An increasingly virtual taking care model and increased consumer adoption came from fundamental shifts in policy at both the government and provider levels.
Since March, state and the most prominent federal regulators have moved quickly to reduce the most dangerous barriers to telehealth.
Understanding and prioritizing these new tools can also speed up the access to which the care is given to the infants while protecting the healthcare workers other community members.
These measures will be opened the floodgates for telehealth, allowing for all the latest programs and expanding existing networks.
More than 30,000 people who used to live in the United States live with cystic fibrosis (CF), a hereditary condition characterized by thick, sticky mucus that clogs airways and traps germs, leading to infections, inflammation, and other complications.
Cystic Fibrosis:
The cystic fibrosis gene mutation is estimated to represent 90 per cent of individuals living with the disease.
Hemoglobinopathies is a rare genetic disease that affects the structure or production of the haemoglobin molecule. This red protein is responsible for transporting the oxygen in the blood cells and the blood.
The most essential and common hemoglobinopathies include sickle cell disease and thalassemia, which combined affect more than 330,0000 children born worldwide every year and more than 100,000 patients with a sickle disorder in the United States alone.
The past research in hemoglobinopathies has brought an experimental gene therapy, giving those who have the condition the potential ability to make functional haemoglobin molecules.
Sickled blood cells:
It reduces the presence of sickled blood cells or ineffective red blood cells in thalassemia prevents associated complications—a novel drug for primary progressive many of sclerosis.
In most individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS), the immune system that has attacked the fatty protective myelin sheath attacks the heavy protective myelin sheath that covers the nerve fibres, causing communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body, permanent damage or deterioration and eventual death.
Approximately 15 per cent of people with Multiple sclerosis experience a disease subset is known as primary progressive characterized by gradual onset and steady progression of signs and symptoms.
Monoclonal Antibody:
A new, FDA approved therapeutic monoclonal antibody with a novel target is the first and only Multiple sclerosis treatment for the primary progressive population.
Stated as excessive bleeding after having a baby, postpartum haemorrhage is a devastating complication of childbirth, affecting from one to five per cent of women who give birth.
Mothers are experiencing postpartum haemorrhage drugs, which may cause dangerous side effects, lengthy uncomfortable procedures and even emergency hysterectomy with loss of fertility.
Non–surgical interventions directed at the bleeding site have been limited to balloon devices that expand the uterus while compressing the bleeding area. But the newest advancement is that of vacuum induced in the uterine tamponade.
This method uses a negative pressure that is created to be created inside the uterus to collapse the bleeding activity causing the muscle to close off the vessels.