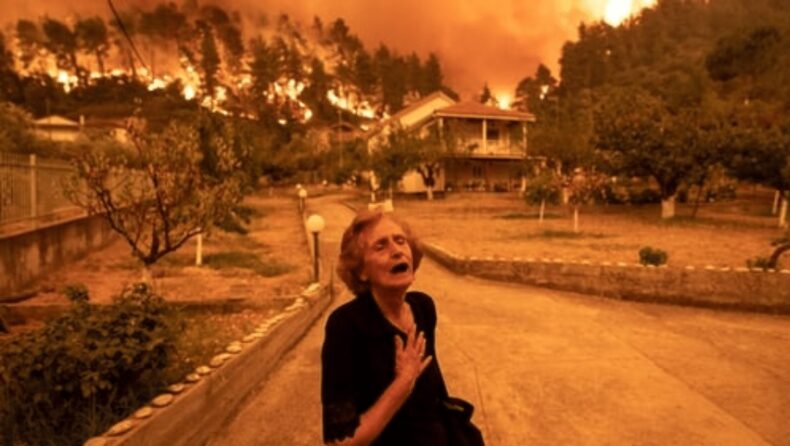
According to estimations, 11,000 extra deaths may have occurred in France and 8,000 in Germany as a result of the record heat that began suffocating Europe in May.
According to estimations, record heat started suffocating Europe in May and may have caused 11,000 more deaths in France and 8,000 in Germany.
According to scientists, severe droughts like the ones this summer in Europe, North America, and China are at least 20 times more likely to occur due to human-caused global warming than they would have been more than a century ago.
It is the most recent proof of how the availability of food, water, and electricity is being threatened by climate change brought on by the combustion of fossil fuels.
According to a recent study, scorching heat throughout much of the Northern Hemisphere was the primary cause of this year’s droughts.
The gradual increase in the planet’s surface temperature is known as global warming. Although this warming trend has been around for a while, the burning of fossil fuels has greatly accelerated its pace over the past century.
The amount of fossil fuels burned has increased along with the size of the human population. Burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas results in the “greenhouse effect,” which affects the atmosphere of Earth.
Without the influence of greenhouse gas emissions, such high average temperatures across such a vast area would have been “nearly inconceivable,” according to the experts.
The scientists discovered that there is now a 1-in-20 possibility that soil conditions as dry as they were this summer will persist throughout the Northern Hemisphere north of the tropics each year. They claimed that this likelihood was raised by global warming.
Maarten van Aalst, the director of the Red Cross Red Crescent Climate Center and one of 21 researchers who prepared the new study as part of the World Weather Attribution initiative, a research collaboration that specialises in quick analysis of extreme weather events, said: “In many of these countries and regions, we are clearly, according to the science, already seeing the fingerprints of climate change.”
On its own, extreme summer dryness that destroys crops, impairs river commerce, and burdens hydropower production would be quite problematic.
However, there have already been other factors driving up food and energy costs globally this year, such as Russia’s conflict in Ukraine.
According to estimations, 11,000 extra deaths may have occurred in France and 8,000 in Germany as a result of the record heat that began suffocating Europe in May.
The area burned by summer wildfires across the European Union was more than twice as vast as it had been on average over the preceding 15 years.
According to the nation’s meteorological agency, China saw its most harsh summer since modern records began in 1961, which decreased hydropower generation in the south’s manufacturing-heavy region.
China consumed more coal to maintain production lines at auto and electronics industries, which increased the country’s contribution to global warming.
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, this summer saw moderate to extreme drought in over half of the lower 48 states in the United States.
The scientists discovered that there is now a 1-in-20 possibility that soil conditions as dry as they were this summer will persist throughout the Northern Hemisphere north of the tropics each year. They claimed that this risk was raised by global warming, although they cautioned…
According to estimations, 11,000 extra deaths may have occurred in France and 8,000 in Germany as a result of the record heat that began suffocating Europe in May.
The area burned by summer wildfires across the European Union was more than twice as vast as it had been on average over the preceding 15 years.
According to the nation’s meteorological agency, China saw its most harsh summer since modern records began in 1961, which decreased hydropower generation in the south’s manufacturing-heavy region.
China consumed more coal to maintain production lines at auto and electronics industries, which increased the country’s contribution to global warming.
The drought that engulfed Europe, China, and North America between June and August was estimated by the World Weather Attribution programme, which determines how closely connected particular weather events are to global warming, to occur once every 20 years at current levels of warming.