Uncovering the Never-Seen-Before Lens Galaxies and Pandora’s Cluster Image
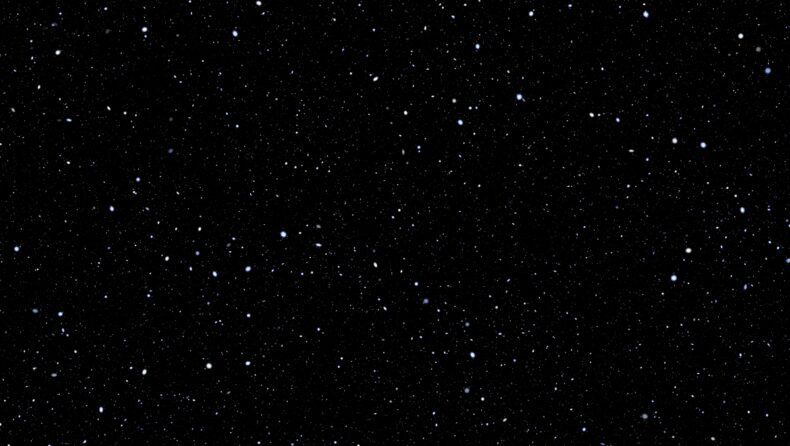
NASA’s James Webb Telescope has helped astronomers reveal a never seen deep-field image featuring Pandora’s Cluster (Abell 2744). Three massive clusters of galaxies are shown coming together to form a mega cluster of galaxies in Webb’s view.
This was achieved by using a natural phenomenon that was discovered by Einstein in 1915, the Theory of Gravity known as General Relativity. This natural phenomenon, that is, gravitational lensing, helped in creating a deep-field view that included extremely old and faint galaxies.
Deep-field observations are long exposures of regions of the sky, that help in showing difficult-to-see objects.
Previously observed image of the region was provided by the Hubble Space Telescope, which gave an assortment of different structures within it, and, therefore only the central core of the image was studied by the telescope.
With the help of the James Webb Telescope and its powerful infrared technology its observation of the cluster has provided an image that was invisible to the human eye.

NASA- How James Webb Space Telescope Helped
The team looked at Pandora’s Cluster by using the telescope’s powerful instruments, Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) with the Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec). These were a part of the Ultradeep NIRSpec and NIRCam ObserVations before the Epoch of Reionisation (UNCOVER) program.
The exposure lasts around four to six hours which gave the UNCOVER team a total of thirty hours of observing time. These observations will be followed up by an analysis of the region with the help of NIRSpec, this will provide a detailed account of measurements of distances within the cluster along with the details of the constituent galaxies, called lensed galaxies, and their composition.
The deep field image was a result of four snapshots by JWST which were stitched together. This gave a panoramic image featuring 50,000 sources of infrared light. This gave the deep-field image of Pandora’s Cluster which is located nearly 3.5 billion light-years away.
This is believed to provide new insights into the early era of evolution and galaxy assembly, which could result in the opening of new boundaries and revolutionizing the study of galactic evolution as astronomers are aiming to achieve a balance of breadth and depth. The data is set to be released this summer.
A co-principal investigator on the UNCOVER Program Ivo Labbe, an astronomer at the Swinburne University of Technology in Melbourne, Australia said that the image of Pandora’s Cluster, provided by Webb, shows a stronger, deeper, and, wider lens which was better than ever seen before.
All of the NIRCam photometric data has been released publicly to get other astronomers familiar with the discovery so that with Webb’s data sheet they can plan their scientific studies.
Gabriel Brammer, Niels Bohr Institutes’s Cosmic Dawn Center, University of Copenhagen, an UNCOVER co-investigator said that they are committed to helping the astronomy community to make the best use of the resource they have in Webb.
Pandora
According to Greek mythology, Pandora was created by Hephaestus by Zeus’s instructions, was the first human woman, whose curiosity led her to open a container that released all of the evils and hardships that now exist in the world.

According to Rachel Benzanson, an astronomer at the University of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, also a co-principal investigator on the UNCOVER program, the myth of Pandora is about the curiosity of humans that set out the past from the future, which, as said by her, is a fitting connection to the opening up of the new realms of the universe by Webb, including the deep-field image of the Pandora’s Cluster.