Oil prices boomed sharply as the world’s largest producer of oil, Saudi Arabia announced that it would bring down the production of oil by million barrels per day from July, to counter the macro-economic challenges posed by the plummeting prices. The move is in addition to the arrangement agreed upon by OPEC+ countries to cut the oil supplies.

Figure 1 Image Source: Getty Images
Why did Saudi Arabia take this decision?
OPEC+ countries met for a seven-hour long meeting where they discussed the issue of dipping oil prices. Other members of the oil-producing countries’ organization also gave consent for reducing oil production to salvage the rising prices. OPEC+ also came out with a decision that the targets would drop down to 1.4 million barrels per day from 2024.

Figure 2 Image Source: Wion
Oil prices saw upward trends on the graph when Russia invaded Ukraine but have retreated to the original state that prevailed from the beginning of the war.
On Sunday, Saudi Energy Minister Prince Abdulaziz bin Salman remarked that Saudi Arabia’s cut of one million barrels per day might be prolonged beyond July if required. He said that “This is a Saudi lollipop” which is seen as a move to equilibrate the world oil market.
Before the meeting of OPEC+, the member states were quite reluctant to lower the output because it was felt that it would jeopardize the oil revenues. Most of the OPEC countries are rentier economies, that is, the countries which are dependent on substantial external rent. Here, in this case, the states are relying on oil for their capital.
But then, Saudi Arabia pitched for the slashing of oil production. From the vantage- point of Saudi Arabia, this settlement is quite beneficial because less oil generation would hike the oil demand which would lead to soaring prices. As a result, more revenue will be earned. More money flowing into the Saudi state would allow it to invest in different projects like Neom because it seeks to diversify its economy as a part of Vision 2030.
On the other hand, it has cast uncertainty for the demand for oil in the next couple of months. Western countries and the USA fear the recession. The West has also shown concern about OPEC’s strategy of manoeuvring the oil prices according to their self-interests and has also accused the organization of supporting Russia in its war against Ukraine though the US has imposed sanctions on the aggressor.
What are OPEC and OPEC+?
OPEC stands for Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries, which traces its inception to 1960 in Baghdad. Founding members include Iraq, Iran, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela. The main objective of this organization is to ensure an uninterrupted supply of petroleum and the stabilization of oil prices. Before the formation of OPEC, the prices were regulated by a “seven-sisters group” of multinational energy firms.
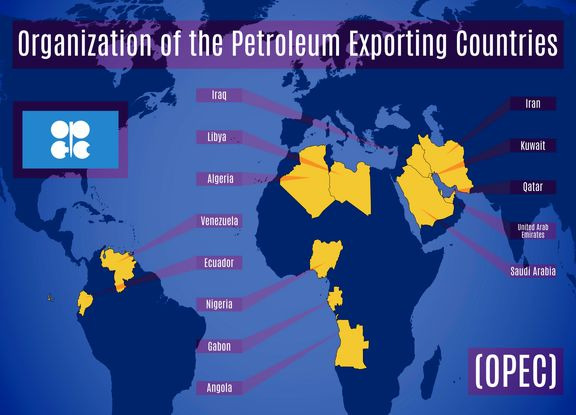
Figure 3 Image Source: Petrotahlil
OPEC at present has 13 members including Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Libya, Nigeria, and the United Arab Emirates, and five other founding members. The organization is headquartered in Vienna.
In 2016, OPEC+ was created adding more countries Russia, Mexico, Oman, Kazakhstan, and Azerbaijan. It brought Russia and Saudi Arabia together against the US shale oil production which had led to a fall in prices of crude oil thereby threatening the oil-producing countries’ livelihood. Interestingly, this group is responsible for the world’s 40% of production of crude oil.
Since oil is an economic tool in the arena of geopolitics, these countries have used their source of revenue to turn the tables in their favour during conflictual situations. One of the prominent examples is that of the 1973 oil crisis which was triggered by the embargo inflicted by OPEC countries against those states including the USA and other Western countries who supported Israel in the Arab-Israeli war of 1973. This led to a manifold increase in oil prices.












