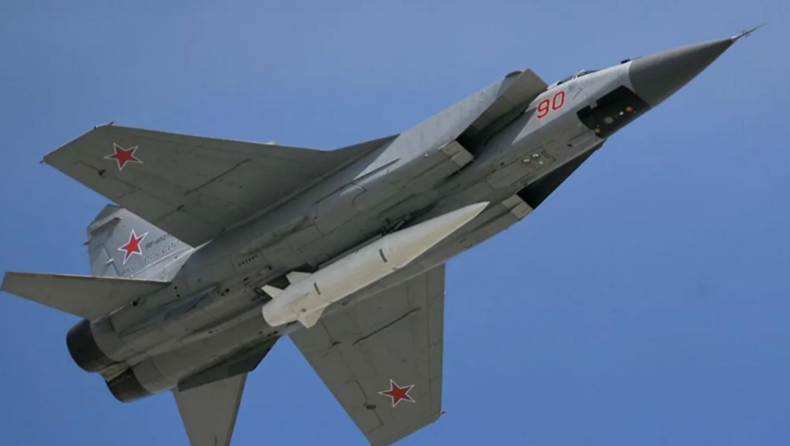
A MiG-31K fighter jet with a Kinzhal hypersonic missile flies over Moscow’s Red Square during the Victory Day military parade in 2018.
The reported use of hypersonic weapons by Russia in Ukraine in recent days is not just an indication that the military is turning to more lethal weapons, but also an opportunity for Russia to show off weapons it claims it has been developing for years.
Last Sunday, the Russian Ministry of Defense declared that it had used a hypersonic missile in the current battle with Ukraine for the first time.
“A vast underground storage containing missiles and aviation ammunition in the village of Deliatyn in the Ivano-Frankivsk region was destroyed by the Kinzhal aviation missile system with hypersonic aeroballistic missiles,” defense ministry spokesperson Igor Konashenkov said.
What is a hypersonic missile and what are the breakthroughs in this technology?
- A hypersonic missile is a manoeuvrable weapon system that travels at least at Mach 5 or five times the speed of sound.
- The hypersonic missile’s manoeuvrability distinguishes it from a ballistic missile, which follows a defined course or ballistic trajectory.
- Hypersonic missiles, unlike ballistic missiles, do not follow a ballistic trajectory and can be manoeuvred to the target.
- Hypersonic Glide Vehicles (HGV) and Hypersonic Cruise Missiles are the two types of hypersonic weaponry systems.
- The hypersonic cruise missile is launched from a rocket before gliding to its target, whilst the HGV is driven by air-breathing high-speed engines or scramjets after attaining its target.
- When other forces are unavailable or denied access, hypersonic weapons, according to General John Hyten, a former Commander of US Strategic Command, can allow responsive, long-range strike options against distant, guarded, or time-critical threats (such as road-mobile missiles).
- He made this statement when speaking before the Armed Services Committee of the United States Congress.
- To destroy unhardened targets or even subsurface facilities, conventional hypersonic weapons solely utilize kinetic energy or energy gained from motion.
Is it possible to detect hypersonic missiles in the air?
- Because of their speed, manoeuvrability, and low altitude of flight, hypersonic missiles, according to a Congressional Research Service assessment on hypersonic missiles released in October 2021, could pose a challenge to detection and defence.
- Ground-based radars or terrestrial radars, according to the paper, cannot identify hypersonic missiles until late in their flight.
- The missile attack responders will have a tough time assessing their choices and attempting to intercept the missile because of the delayed detection.
- Some analysts have said that the US’s present missile defence command and control paradigm would be unable of processing data quickly enough to respond to and neutralize an incoming hypersonic missile, according to the Congressional study.
Which countries have or are developing hypersonic weapons?
- Aside from Russia, which debuted its hypersonic missile ‘Kinzhal’ or Dagger in 2018 and has recently deployed it for the first time in combat in Ukraine, China is also said to have this weapon system and has used it twice to round the globe before landing near a target in August 2021.
The Russian Kinzhal missile, a variant of the Iskander missile, was tested in July 2018 from a MiG-31 aircraft and hit a target 500 miles distant.
- According to Russian media estimates, when fired from a MiG-31, the Kinzhal can reach Mach 10 and has a range of up to 1200 miles.
- Russia is also claimed to be employing the missile on the Su-34 long-range fighter and is developing a Tu-22M3 strategic bomber to carry it.
- In August 2021, China reportedly tested an HGV using a Long March rocket. China is said to be considering using this military system by combining conventionally armed HGVs with its DF-21 and DF-26 missiles.
- China is also believed to have fielded the DF-ZF HGV, which has a range of 1200 miles. China successfully tested Starry Sky-2 (Xing Kong-2), a nuclear-capable hypersonic vehicle prototype in August 2018, according to US defence officials referenced in the Congressional report.
- Hypersonic weapons are being developed in the United States as part of the Navy’s conventional Prompt Strike Program, as well as the Army, Air Force, and Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA).
- While the United States, Russia, and China are developing hypersonic missiles, India, France, Germany, Japan, and Australia are all working on them.
About Indian hypersonic missile programme?
- “SHAURYA” is a canister launched hypersonic surface-to-surface tactical missile developed by the Indian Defence and Research organization (DRDO).
- According to the Congressional report, as part of its Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle programme, India is developing an indigenous, dual-capable (conventional and nuclear) hypersonic cruise missile and has successfully tested a Mach 6 scramjet in June 2019 and September 2020. According to the study, “India operates roughly 12 hypersonic wind tunnels and is capable of testing speeds up to Mach 13.”
Published by : Aditya Andharia
Edited By : Kritika Kashyap