Meteorologists predict that Europe is now experiencing the worst drought in the last 500 years.
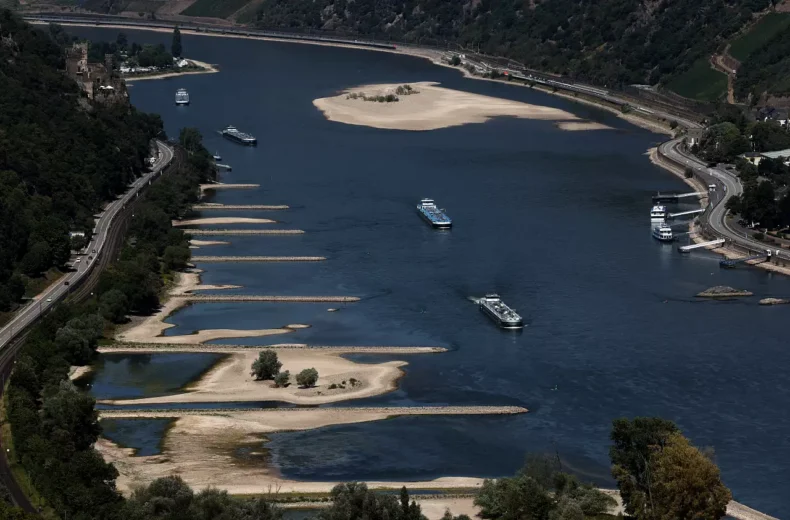
The Loire of France and the Rhine river flowing in several Western European countries are drying up fast.
The Italian river Po water level has decreased by 2 meters. The second longest river in Europe, the Danube is also experiencing the first signs of drought.
The European continent can’t seem to catch a break since the start of this year. The beginning of the year started with the Russian-Ukraine war, followed by intense heat waves, and now the onslaught of drying rivers.
The once mighty rivers of Europe are becoming arid which will have huge impacts on crop production, industry, and supply shortages as well as heavy consequences for the millions of people dependent on these rivers.
The droughts in Europe were predictable after the dry winters, record-breaking summer temperatures with overbearing heat waves, and the waterways of Europe were left to be overheated, resulting in the current drought conditions.
For the past two months, no signs of rainfall have been recorded in Europe, including the western, central, and southern parts.
As the drought is still ongoing, there is not much information regarding the exact situations and consequences the drought will have, says Andrea Torti, a member of the European Commission’s Joint Research Center.
“There are high risks of dry conditions and without effective mitigation in the next three months, the drought intensity and frequency will rapidly increase all over Europe.”
The rivers of Europe

The aforementioned Rhine river is the vital artery of Europe; the energy supply, freight transportation, irrigation, manufacturing, and drinking water supply of several countries like Germany, France, and Switzerland are all dependent on this particular waterway.
At least 30-40% of Italy’s agricultural production depends on the Po river. There have been warnings from the paddy field farmers that almost 60% of rice crops are lost if the river water runs out.
Norway, the country reliant on hydro-power for at least 90% of its power supply, is also reported to be facing the problem of water shortage.
The drought will have heavy implications on the economies of several European countries.
New dusk for Europe
There have been red alerts for at least every day, and around 63% of Europe’s land has alerts for drought warnings. Europe has been burning up since its last heat wave and now even the waters are drying up.
The problems that the pandemic slowdown as well as the ongoing Russian-Ukraine war have caused have still not been resolved.
The climate crisis is seemingly bringing in its sorts of problems that might take decades to even understand as the research for changing climates is scarce.
The climate crisis

The apocalyptic climate doom seems to have started. Scientists have predicted that the process of climate change will just start more rapidly in the coming years.
Not only will the human population suffer, but wildlife will also be hit by the changes in the global temperature.
Some of the worst hit regions would be countries like Indonesia, India, and other developing or under-developed nations.
Agricultural production will be affected as the scarcity of water due to drought increases.
India and other developing nations would also be hit with severe consequences which will affect at least more than 2 billion people worldwide. The group that will suffer the most would be the ones who are barely able to afford a means of living and live in shelters outside of the main cities. Bangladesh’s immigration crisis due to flooding is a good but hard-hitting example of climate change’s severity.
Climate change is not a topic that is often brought up during conversations and that needs to be changed. People should be aware of what the impact of climate change would be shortly.
People must start talking about climate change and increase awareness to reduce their carbon footprint, encourage healthy discussions around precautions about global warming, droughts, increasing sea levels, etc.