- The First 3D-printed rocket suspended the latest attempt at its debut rocket launch on Saturday.
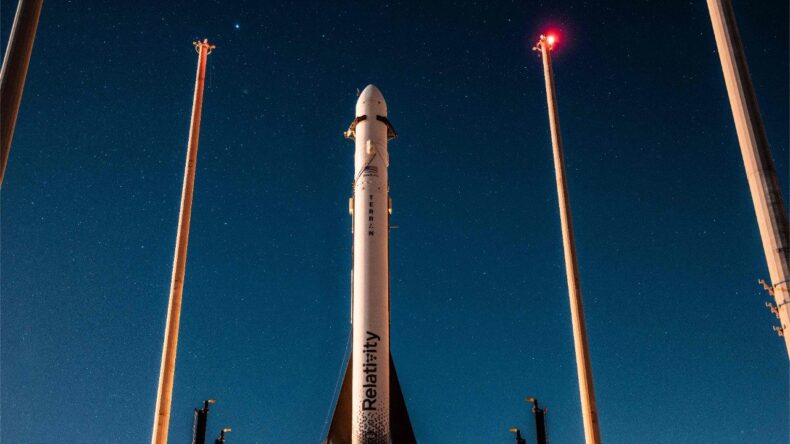
- Relativity Space manufactures the first 3D-printed rocket named Terran 1.
- It will supposed to launch from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station after deciding on a new time.
The world’s first 3D-printed rocket was planned to launch from Florida on 11th March Saturday. But the launch is cancelled last minute due to an automation issue. Initially, it was planned to take off on 8th March, Wednesday. But the take-off was abruptly postponed due to propellant temperature concerns. According to media reports, the unmanned Terran 1’s rocket encountered the problem. Its engine had already started to ignite. The problem finally caused its takeoff to be canceled for the second time in less than a week.
Table of Contents
The Terran-1 Rocket
Relativity has yet to disclose a new launch date or time; it is unclear what caused the launch engineers to stand down. The Terran-1 is on the first mission of innovative technology that is less expensive to build and fly. Terran 1 is intended to enter low Earth orbit eight minutes after launch. The rocket is on a mission to collect data and demonstrate its ability to withstand the challenges of launch and space travel.
According to Relativity Space, if the rocket successfully reaches low Earth orbit. It will become the first privately-funded methane-fueled spaceship. The Terran 1 has yet to carry a payload on its initial launch. But it can launch as much as 2,755 pounds into low Earth orbit. It is dimension 110 feet (33.5 meters) in height and 7.5 feet (2.2 meters) in diameter. It is made of 3D-printed metal alloys, including the engines, with 85 percent of its bulk.
According to the Long Beach-based industry, it is the largest 3D-printed object ever. The company’s objective is to create a rocket that is 95% 3D printed.
According to Relativity, the liquid oxygen and liquid natural gas used in Terran 1’s Aeon engines are the “propellants of the future,” with the potential to power a trip to Mars one day. The Starship from SpaceX and United Launch Alliance are developing Vulcan rockets. Terran 1 consist of nine three dimensionally printed Aeon 1 engines and one 3D-printed Aeon engine with vacuum in its first stage.
Constructed in 60 days
However, Relativity Space is constructing the Terran R, a more powerful rocket. It can launch a payload weight of 44,000 pounds in low-Earth orbit. The first Terran R from Relativity Space will be completely recyclable. It will launch from Cape Canaveral as per schedule. Relativity Space aims to reduce the waiting time by using its 3D-printed rockets. Because of its excellent cost-effectiveness, radical flexibility, and customizability, 3D printing has the potential to democratize space more quickly, according to the business.
Relativity Space states that Terran 1 and Terran R can be manufactured from a base in less than 60 days. It can be reused 100 times more than fundamental rockets.

Mr. Tim Ellis, CEO of Relativity Space, commented that the company has already inked commercial launch contracts worth $1.65 billion, most of which are for the Terran R.
With the severe launch deficit in this payload class over the ensuing decade, the medium-heavy lift is unquestionably where the most incredible market opportunity lies.
In 2015, Relativity Space was established, with its main office in Long Beach, California. Up to 2,756 pounds can be carried by the Terran 1 and delivered to low-Earth orbit. According to company representatives, the company’s 3D-printed rockets will provide a very inexpensive way to launch tiny commercial satellites into space.