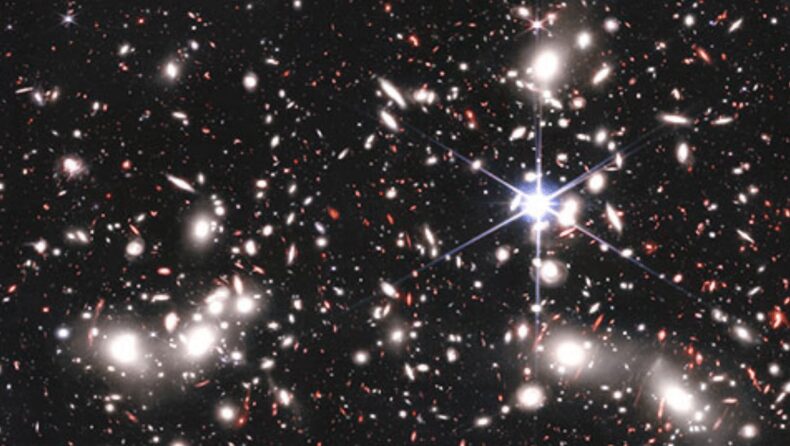
NASA’s James Webb Telescope has yet again come a long way by drawing attention to the highly anticipated and enigmatic Abell 2744 – Pandora cluster. The powerful telescope focused on the cosmic region and unraveled the concealed elements through a recent field image – three massive clusters of galaxies amalgamating to a mega cluster. This cluster’s combined mass generates a massive gravitational lens, a natural magnification effect of gravity, enabling far more distant galaxies in the early universe to be detected by using the cluster as a magnifying glass.
Brief Insight to Pandora Cluster
Abell 2744, often known as Pandora’s Cluster, is a massive galaxy cluster formed from the simultaneous accumulation of at least four independent and small galaxy clusters over the course of 350 million years. It was dubbed ‘Pandora’s Cluster’ due to the wide spectrum of bizarre phenomena released by the impact. Astronomer Rachael Bezanson rightly put out that the ancient narrative of Pandora is thoroughly about human inquisitiveness and revelations that distinguish the past from the future in context to the fitting relation to the ‘new web of cosmos’ that the Webb telescope has captured. The recent field image of the Pandora Cluster is a result of four Webb photos merged to form one panoramic image which details 50,000 points of new infrared light and reveals ‘hundreds of distant lensed galaxies’ in faint elliptical lines.

Einstein’s Theory Of Relativity
A deep look at the JSWT’s masterpiece will reveal a brilliant foreground star from the Milky Way prominent in the picture with unique diffraction spikes. It is surrounded by bright white light sources that are encircled by a haze; these are the considerably more distant galaxies of Pandora’s Cluster. Though human-created equipment is required to observe this cluster of clusters, astronomers also relied on a natural phenomenon originally unveiled by Albert Einstein in his 1915 opus,’ general relativity’, the theory of gravity. According to general relativity, things with mass have an influence on the fundamental fabric of space, bending it. This is similar to laying items on a stretched rubber sheet and making dents in it. Similarly to how balls of increasing mass cause greater, more dramatic dents in that sheet, cosmic objects of enormous mass cause huge warps in the fabric of space. This curvature can be so great that light’s path through it is similarly curved. The foreground mass item, also known as a “lensing object,” can sometimes assist enhance the light from background objects. This amplification allows the already strong JWST to glimpse light from distant and hence early galaxies that would be too weak to discern without lensing.

Collaboration of Hubble and James Webb Telescope
Pandora’s central core was earlier analysed by the Hubble Space Technology. One drawback was it could not image lens core to the lower right and thus was soon accompanied by the high sensitivity Webb telescope as astronomers intended to achieve a balanced combination of breadth and depth by combining the latter’s strong infrared detectors with a large mosaic picture of the region’s many zones of lensing. This was believed to open up a new frontier in the study of cosmology and galactic evolution.
Uncover Program Detailing
Astronomers studied Abell 2744 as part of the UNCOVER program- Ultra-deep NIRCam and NIRSpec Observations Before the Epoch of Reionization. On the other hand Webb is a joint program from NASA, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. The collaboration of both brought in a spectacular result. Firstly, The UNCOVER team captured the cluster using Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), with exposures lasting 4-6 hours for a total of around 30 hours of viewing time. The next step, is awaited, will be to meticulously go through the imaging data and select galaxies for follow-up observations with the Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), which will provide precise distance measurements as well as other detailed information about the compositions of the lensed galaxies, providing new insights into the early era of galaxy assembly and evolution. The UNCOVER team anticipates carrying out these NIRSpec observations within the summer of 2024.