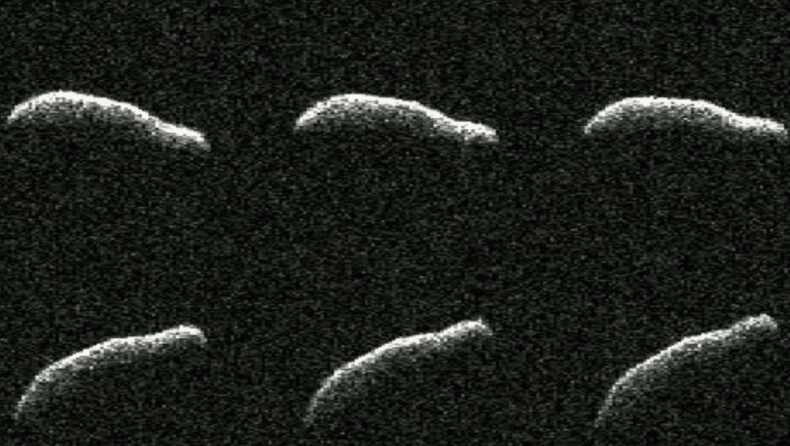
The NASA team recently witnessed the 2011 asteroid, 2011AG5, again on the 19 th of February 2024 with dimensions very similar to the Empire State Building,1600 metre long and 500 metre wide. Astronomers have taken note of the asteroid because of its lengthy form after it recently flew past Earth. It is one of the most extended asteroids ever discovered till date.
Discovery
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California kept a careful eye on the oblong shaped asteroid 2011 AG5. It is equivalent in size to the Empire State Building. The Deep Space Network’s station in Barstow, California, has a strong 230-foot (70-metre) Goldstone Solar System Radar antenna dish that was used to determine the size of this elongated asteroid. Lance Benner, a principal scientist at JPL who assisted in leading the observations, stated that among the 1,040 near-Earth objects that planetary radar has spotted so far, this is one of the most elongated things that they have ever seen.

Image Insights
The photograph of the asteroid was taken six times to create a mosaic by the Goldstone Solar System Radar antenna dish in California. The photograph gives an appearance of being scooped on one side, is a dark charcoal hue, and gently rotates every nine hours. It includes subtle dark and brighter patches that could point to small-scale surface features, a few dozen metres wide, as well as a massive, broad concavity in one of the body’s two hemispheres. The asteroid would seem as black as charcoal to the human eye as well. Astronomers are scrupulously working on getting further analysis.
Research
February 3 was marked as a turning point as several NASA along with other agencies witnessed the passage of this humongous asteroid. Although at that point of time this asteroid colliding with earth seemed bleak, scientists at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory kept their eyes wide open and collected information pertaining to it such as dimensions, surface features and rotational speed. On further scrutiny it was found that it has an orbit of 621 days around the sun and has thrice the distance of earth and moon according to the NASA’s Centre for Near Earth Object Studies (CNEOS).

Question of an asteroid hit
2011 AG5 soon after its discovery was marked ‘poster child asteroid’ with no future impact but its later trajectory shows signs of an impact between 2040 and 2047. Although an asteroid hit is currently termed uncertain . Asteroid hits do happen once or twice in a century, the 2013 asteroid hit was quite massive in that scenario. The greatest asteroid to hit Earth in more than a century was Chelyabinsk. A 20-metre, 13,000-ton asteroid that was travelling at a speed of more than 18 km/s entered the atmosphere over the Ural Mountains in Russia just after daybreak on a beautiful winter day.
Further exploration
Millions of asteroids orbit the sun. These are the rocky debris that was left over when the solar system formed some 4.6 billion years ago. The majority of that prehistoric debris is too far away to be a danger to Earth.The bulk of asteroids are located in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, although periodically boulders are pushed into the inner solar system, which is comparatively closer to Earth. There are no known asteroids that are headed straight for Earth. Yet, there are 30,000 gigantic objects in the universe that scientists are closely monitoring. They also believe there may be another 15,000 or so objects that are still undiscovered. Astronomers are discovering roughly 500 new large space objects in the Earth’s solar system using sophisticated telescopes to survey the sky.